3D printing the first ever biomimetic tongue surface
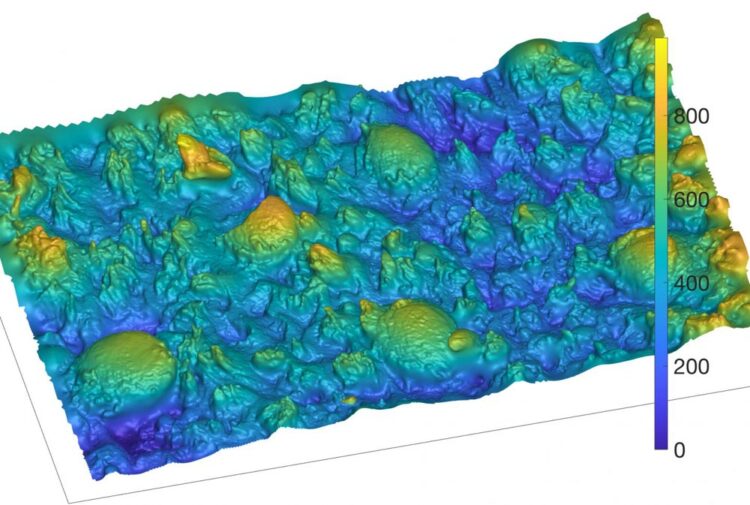
3D optical image close to the tip of human tongue surface
Credit: Anwesha Sakar, University of Leeds
Scientists have created synthetic soft surfaces with tongue-like textures for the first time using 3D printing, opening new possibilities for testing oral processing properties of food, nutritional technologies, pharmaceutics and dry mouth therapies.
UK scientists led by the University of Leeds in collaboration with the University of Edinburgh have replicated the highly sophisticated surface design of a human tongue and demonstrated that their printed synthetic silicone structure mimics the topology, elasticity and wettability of the tongue’s surface.
These factors are instrumental to how food or saliva interacts with the tongue, which in turn can affect mouthfeel, swallowing, speech, nutritional intake and quality of life.
A biomimetic tongue will help developers to perform screening of newly designed products and accelerate the new development processes without the necessity of human trials at early stages that are often very expensive and time consuming.
Particularly, since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, social distancing has posed significant challenges to carry out such sensory trials and consumer tests. A biomimetic tongue will be immensely helpful to increase development productivity and reducing manufacturers’ reliance on human trials in the early stages.
A biomimetic tongue could further offer myriad applications to fight against adulteration in food and other orally administered pharmaceutics whether textural attributes are governing features and can save huge economic loss.
The complex nature of the tongue’s biological surface has posed challenges in artificial replication, adding major obstacles to the development and screening of effective long-lasting treatments or therapies for dry mouth syndrome — roughly 10% of the general population and 30% of older people suffer from dry mouth.
Study lead author, Dr Efren Andablo-Reyes conducted this research while a postdoctoral fellow in the School of Food Science and Nutrition at Leeds. He said: “Recreating the surface of an average human tongue comes with unique architectural challenges. Hundreds of small bud-like structures called papilla give the tongue its characteristic rough texture that in combination to the soft nature of the tissue create a complicated landscape from a mechanical perspective.
“We focused our attention on the anterior dorsal section of the tongue where some of these papillae contain taste receptors, while many of them lack such receptors. Both kinds of papillae play a critical role in providing the right mechanical friction to aid food processing in the mouth with the adequate amount saliva, providing pleasurable mouthfeel perception and proper lubrication for swallowing.
“We aimed to replicate these mechanically relevant characteristics of the human tongue in a surface that is easy to use in the lab to replicate oral processing conditions.”
The study that brought together unique expertise in food colloid science, soft matter physics, dentistry, mechanical engineering and computer science is published today in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
The team took silicone impressions of tongue surfaces from fifteen adults. The impressions were 3D optically scanned to map papillae dimensions, density and the average roughness of the tongues. The texture of a human tongue was found to resemble a random layout.
The team used computer simulations and mathematical modelling to create a 3D-printed artificial surface to function as a mould containing wells with the shape and dimensions of the different papillae randomly distributed across the surface with right density. This was replica-moulded against elastomers of optimised softness and wettability.
University of Edinburgh co-author, Rik Sarkar of the School of Informatics said: “The randomness in distribution of papillae appears to play an important sensory role for the tongue.
“We defined a new concept called collision probability to measure mechanosensing that will have large impact in this area. In the future, we will use a combination of machine learning and computational topology to create tongue models of diverse healthy and diseased individuals to address various oral conditions.”
The artificial surface was then 3D printed using digital light processing technology based in the School of Mechanical Engineering at Leeds.
The team ran a series of experiments using different complex fluids to ensure that the printed surface’s wettability – how a liquid keeps contact and spreads across a surface – and the lubrication performance was the same as the human tongue impressions.
Co-author Dr Michael Bryant from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Leeds said: “The application of bio-tribological principles, the study of friction and lubrication, in the creation of this tongue-like surface is a significant step forward in this field.
“The ability to produce accurate replicas of tongue surfaces with similar structure and mechanical properties will help streamline research and development for oral care, food products and therapeutic technologies.”
Principal Investigator Anwesha Sarkar, Professor of Colloids and Surfaces at Leeds, said: “Accurately mapping and replicating the tongues surface and combining that with a material that approximates the elasticity of human tongue was no small task. Harnessing expertise from multiple STEM disciplines, we’ve demonstrated the unprecedented capability of a 3D printed silicone surface to mimic the mechanical performance of the human tongue.
“We believe that fabricating a synthetic surface with relevant properties that mimics the intricate architectural features, and more importantly the lubricating performance of the human tongue is paramount to gaining quantitative understanding of how fluids interact within the oral cavity.
“This biomimetic tongue surface could also serve as a unique mechanical tool to help detect counterfeit in food and high-valued beverages based on textural attributes, which is a global concern and can help to ensure food safety.
“Ultimately, our hope is that the surface we have designed can be important in understanding how the biomechanics of the tongue underpin the fundamentals of human feeding and speech.
###
Further information:
This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program
The paper ‘3D Biomimetic Tongue-Emulating Surfaces for Tribological Applications’ is published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on 27 October 2020 (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c12925)
For additional information contact University of Leeds press office
Anna Harrison
a.harrison@leeds.ac.uk
List of all images and video available:
Image:
Masks_ palate&tongue
Caption: Silicone impressions of human palate and tongue. Human tongue impressions were collected from 15 healthy subjects in the morning, at least two hours since eating and drinking.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Image:
3Dimage_HumanTongue
Caption: Negative 3D optical images of the tongue impressions taken using (a) hydrophobic (polyvinyl siloxane mould) and (b) hydrophilic (alginate) masking materials where the papillae are visible as circular holes.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Image:
Impression_PigsTongue
Caption: Silicone impression of pigs tongues were used to further understand structural architecture of tongue surface.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Image:
PigsTongue_ Scanning electron microscopy
Caption: Scanning electron microscopy of pig tongue.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Image:
Biomimtic_TongueSurface
Caption: 3D optical image close to the tip of human tongue surface.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Image:
Fungiform_BiomimticTongue
Caption: fungiform papillae with their characteristic dome shape.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Image:
3Dprinter Caption: Digital light processing technology 3D printer, School of Mechanical Engineering University of Leeds.
Credit: University of Leeds
Image:
Tongue_mould
Caption: The 3D printed negative mould showing holes for the filiform and fungiform papillae.
Credit: University of Leeds
Image:
Biomimetic_tongue
Caption: Biomimetic tongue.
Credit: University of Leeds
Video:
SurfaceDeformation
Caption: Show the difference in rigidity between polydimethylsiloxane (left) previously used as artificial tongue-surfaces and the new polymer used by the team (right). The softer polymer is a better approach to the biological tissue.
Credit: Anwesha Sarkar, University of Leeds
Video:
BiomimeticTongue_deformation
Caption: Short video showing how the biomimetic tongue deforms.
Credit: University of Leeds
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is one of the largest higher education institutions in the UK, with more than 38,000 students from more than 150 different countries, and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universities. The University plays a significant role in the Turing, Rosalind Franklin and Royce Institutes.
We are a top ten university for research and impact power in the UK, according to the 2014 Research Excellence Framework, and are in the top 100 of the QS World University Rankings 2021.
The University was awarded a Gold rating by the Government’s Teaching Excellence Framework in 2017, recognising its ‘consistently outstanding’ teaching and learning provision. Twenty-six of our academics have been awarded National Teaching Fellowships – more than any other institution in England, Northern Ireland and Wales – reflecting the excellence of our teaching. http://www.
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



