A new iron-based superconductor stabilized by inter-block charger transfer
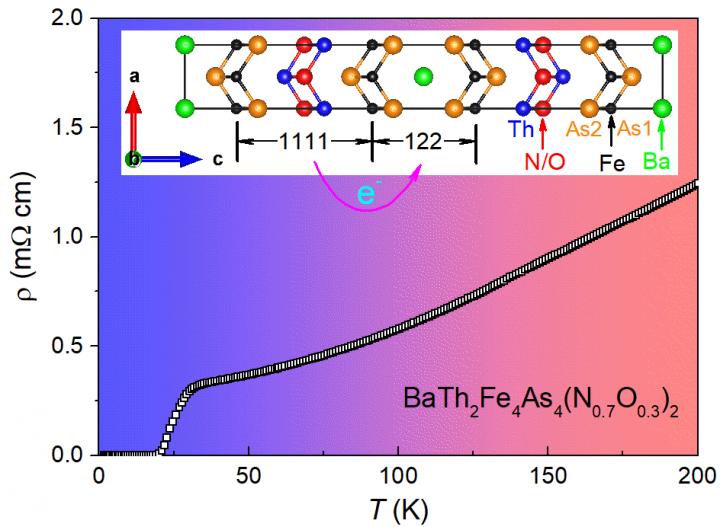
Temperature dependence of electrical resistivity for the BaTh2Fe4As4(N0.7O0.3)2 sample, indicating a superconducting transition at 30 K. The zero-resistance temperature is 22 K. The inset shows the crystal structure projected on the ac plane. The two constituent structural blocks, named "1111" and "122" respectively, are marked, and the inter-block charge transfer is shown by the arrow. Credit: ©Science China Press
The newly discovered electron-doped IBSC is BaTh2Fe4As4(N0.7O0.3)2, an intergrowth compound of un-doped BaFe2As2 and electron-doped ThFeAsN0.7O0.3 (see the inset of Figure 1). The new superconductor could be synthesized only when nitrogen is partially replaced with oxygen as in the case of BaTh2Fe4As4(N0.7O0.3)2.
Namely, the oxygen-free phase, BaTh2Fe4As4N2, could not be prepared albeit of the lattice matching. The realized synthetic process is actually a redox reaction, BaFe2As2 + 2ThFeAsN0.7O0.3 = BaTh2Fe4As4(N0.7O0.3)2, which indicates an essential role of inter-block charge transfer for stabilizing the intergrowth structure.
Note that, while both the constituent structural blocks share identical iron atoms, they contain crystallographically different arsenic atoms, as a consequence of the charge transfer.
Although the new superconductor is isostructural to the previous “12442-type” ones, it shows contrasting structural and physical properties. First, the structural details in the FeAs layers are different from those of hole-doped 12442-type IBSCs, but similar to most electron-doped IBSCs.
Second, the Hall-effect measurement shows negative Hall coefficient in the whole temperature range, and the Hall coefficient values are consistent with the electron doping level due to the oxygen substitution. Third, the superconducting properties such as the upper critical fields and specific-heat jump are close to most electron-doped IBSCs.
The onset resistive transition temperature of the new double-FeAs-layer IBSC is 30 K, and the zero-resistance temperature is 22 K. Correspondingly, the magnetic susceptibility and specific-heat data suggest two transitions, and the bulk superconductivity appears at 22 K. The result is in contrast with the single-FeAs-layer counterpart, ThFeAsN0.85O0.15, with the same doping level. The latter does not show superconductivity above1.8 K.
The essential role of inter-block charge transfer demonstrated seems to be insightful, which could be helpful for the exploration of broader layered materials beyond the layered IBSCs.
###
See the article: Ye-Ting Shao, Zhi-Cheng Wang, Bai-Zhuo Li, Si-Qi Wu, Ji-Feng Wu, Zhi Ren, Su-Wen Qiu, Can Rao, Cao Wang and Guang-Han Cao,”BaTh2Fe4As4(N0.7O0.3)2: an iron-based superconductor stabilized by inter-block-layer charge transfer,” Sci. China Mater. (2019) doi: 10.1007/s40843-019-9438-7
This article was published online (http://engine.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40843-019-9438-7All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



