All wired up: New molecular wires for single-molecule electronic devices
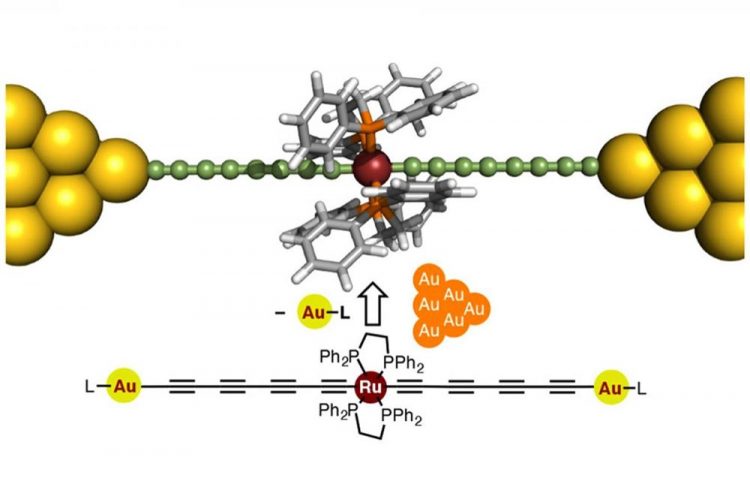
The proposed wire is 'doped' with a ruthenium unit that enhances its conductance to unprecedented levels compared with previously reported similar molecular wires. Credit: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Since their conception, researchers have tried to shrink electronic devices to unprecedented sizes, even to the point of fabricating them from a few molecules.
Molecular wires are one of the building blocks of such minuscule contraptions, and many researchers have been developing strategies to synthesize highly conductive, stable wires from carefully designed molecules.
A team of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology, including Yuya Tanaka, designed a novel molecular wire in the form of a metal electrode-molecule-metal electrode (MMM) junction including a polyyne, an organic chain-like molecule, “doped” with a ruthenium-based unit Ru(dppe)2.
The proposed design, featured in the cover of the Journal of the American Chemical Society, is based on engineering the energy levels of the conducting orbitals of the atoms of the wire, considering the characteristics of gold electrodes.
Using scanning tunneling microscopy, the team confirmed that the conductance of these molecular wires was equal to or higher than those of previously reported organic molecular wires, including similar wires “doped” with iron units. Motivated by these results, the researchers then went on to investigate the origin of the proposed wire's superior conductance.
They found that the observed conducting properties were fundamentally different from previously reported similar MMM junctions and were derived from orbital splitting. In other words, orbital splitting induces changes in the original electron orbitals of the atoms to define a new “hybrid” orbital facilitating electron transfer between the metal electrodes and the wire molecules. According to Tanaka, “such orbital splitting behavior has rarely been reported for any other MMM junction”.
Since a narrow gap between the highest (HOMO) and lowest (LUMO) occupied molecular orbitals is a crucial factor for enhancing conductance of molecular wires, the proposed synthesis protocol adopts a new technique to exploit this knowledge, as Tanaka adds “The present study reveals a new strategy to realize molecular wires with an extremely narrow HOMO?LUMO gap via MMM junction formation.”
This explanation for the fundamentally different conducting properties of the proposed wires facilitate the strategic development of novel molecular components, which could be the building blocks of future minuscule electronic devices.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles
Humans vs Machines—Who’s Better at Recognizing Speech?
Are humans or machines better at recognizing speech? A new study shows that in noisy conditions, current automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems achieve remarkable accuracy and sometimes even surpass human…

Not Lost in Translation: AI Increases Sign Language Recognition Accuracy
Additional data can help differentiate subtle gestures, hand positions, facial expressions The Complexity of Sign Languages Sign languages have been developed by nations around the world to fit the local…

Breaking the Ice: Glacier Melting Alters Arctic Fjord Ecosystems
The regions of the Arctic are particularly vulnerable to climate change. However, there is a lack of comprehensive scientific information about the environmental changes there. Researchers from the Helmholtz Center…



