
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba have harnessed the strength of bagworm silk to produce a strong conductive fiber. To obtain this novel fiber, the research team combined bagworm silk with polyaniline as a conducting polymer. The composite fibers act as an optical waveguide and are suitable for use in textile transistors. This production of a bagworm silk/polyaniline composite will enable the use of biocompatible conducting fibers for applications ranging from microelectronics to biomedical engineering.
Credit: University of Tsukuba
Stronger than spider silk …
Using natural silk from bagworms and a synthetic conducting polymer, researchers at the University of Tsukuba have developed a strong conducting fiber that demonstrates promise for flexible electronic materials.
Think spider silk is strong? Recent work has shown that bagworm silk is superior to spider silk in both strength and flexibility. Building on these findings, a research team at the University of Tsukuba, led by Professor Hiromasa Goto, has harnessed the strength of bagworm silk to produce a strong, flexible, conductive fiber. This research may lead to new flexible electronic devices, such as wearable electronic materials.
Owing to its high flexibility and strength, spider silk has received much attention for uses ranging from medicine to aerospace applications. By combining natural silk, such as spider silk, with synthetic conductive polymers, researchers can produce textiles with conduction, light emission, and photovoltaic functions. It is also possible to create biocompatible materials that can be used in regenerative medicine and biomedical materials. “We’ve taken the next step from previous research efforts by utilizing the strongest known natural fiber – bagworm silk,” explains Professor Goto.
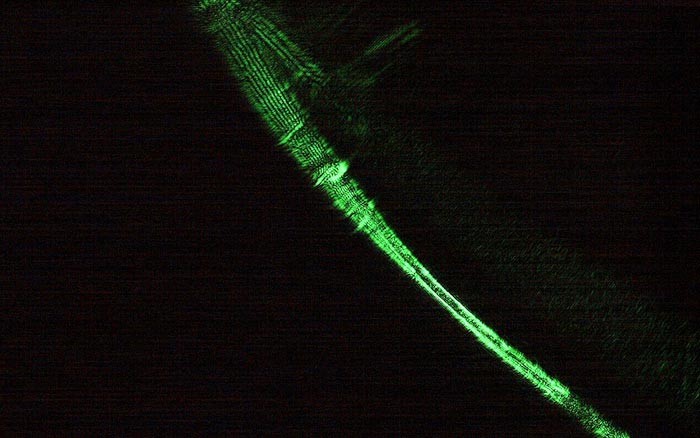
In this study, the research team combined polyaniline, a conducting polymer that can be easily synthesized, with bagworm silk obtained from a bagworm nest. The composite fibers obtained from the silk and polyaniline were 2 microns in diameter and acted as optical waveguides. The investigators demonstrated that green laser light propagates along these fibers, while remaining confined within each fiber. To determine the magnetic properties of the material, the investigators performed superconducting interference device (SQUID) measurements. The results revealed that the composite fibers can act as paramagnets: the fibers become magnetized when placed in an external magnetic field. By applying the bagworm silk/polyaniline composite in a field-effect transistor device, the research team also confirmed that the composite fiber is suitable for use in textile transistors.
As illustrated by this work, the strength of bagworm silk and the conductive properties of polyaniline can be combined, resulting in a new flexible material with desirable characteristics. “With the mass production of bagworm silk,” says Professor Goto, “these fibers can be developed for various practical applications—for example, as electromagnetic inference shields, conductive textile wires, and anticorrosion textiles.” This successful production of a strong conductive fiber comprised of bagworm silk and polyaniline will pave the path toward the application of these fibers in a variety of fields such as tissue engineering and microelectronics.
The article “Preparation of bagworm silk/polyaniline composite” was published in Journal of Applied Polymer Science at DOI: 10.1002/app.51791.
Funding: This research was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 20K05626).
Journal: Journal of Applied Polymer Science
DOI: 10.1002/app.51791
Article Title: Preparation of bagworm silk/polyaniline composite
Media Contact
Naoko Yamashina
University of Tsukuba
kohositu@un.tsukuba.ac.jp














