First Confirmation of New Theory by Metamaterial
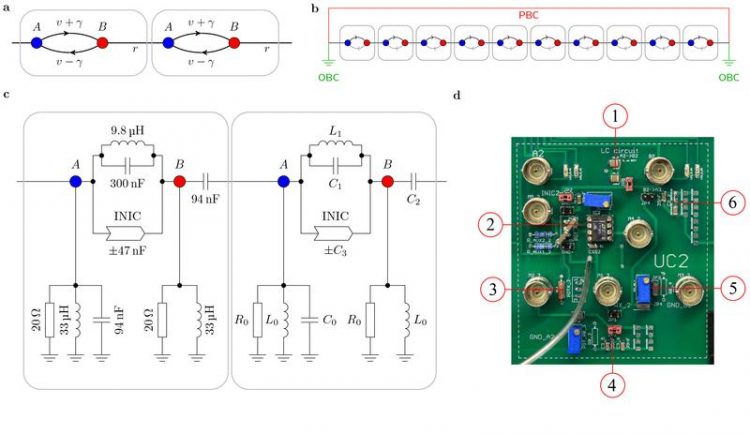
A unit cell cutout of the circuit board, which was built to demonstrate the non-Hermitian skin effect, and the underlying theoretical non-Hermitian model. Tobias Helbig, Tobias Hofmann
Topological metamaterials are applied as a novel platform to explore and study extraordinary effects. Instead of using natural materials, researchers artificially arrange the constituents of a topological metamaterial in a regular structure.
Such an arrangement is analogous to a solid state in which the atoms form a crystal lattice. Usually, these platforms are used to simulate particular properties of solids in order to make them amenable to experimental investigation.
Physicists at Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, perform research on those topological metamaterials, a central scheme of the Würzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat – Complexity and Topology in Quantum Matter.
Novel topological phenomena
A related motif of solid state research in Würzburg is the discovery and characterization of novel topological phenomena. This concerns the study of topological insulators, which are insulating in the bulk, but feature conducting surface states.
Scientists worldwide engage in intensive research on these materials as they exhibit compelling physical phenomena. One day, this research may lead to advances in semiconductor technology or in other fields.
The JMU researchers report on their newest results in the journal Nature Physics. Topological insulators are usually considered as isolated (Hermitian) systems. In contrast, scientists can tweak topological metamaterials such as to study the implications of energy exchange with the environment.
These interactions influence the behaviour of the system from the outside, as would be the case for friction. This way, they experimentally verified the non-Hermitian skin effect (NHSE) previously predicted in theory.
All states localize at the edge
The NHSE involves that, in contrast to a common topological insulator, not only a small fraction but all states of the material appear at its edge, i.e. are localized there. This is described by Tobias Helbig and Tobias Hofmann, the joint first authors of the publication. They are both PhD students in the research group of Professor Ronny Thomale, head of the JMU Chair of Theoretical Physics I.
“Our research shows, among other things, that the physical principles known from isolated solid state systems need to be fundamentally modified in the non-Hermitian case,” the PhD students explain. The new findings would not yet have a direct application. However, they do have the potential to improve highly sensitive optical detectors, as an example.
Electric circuits as a center of innovation in basic research
The experiments leading to the new results were conducted with the group of Dr. Tobias Kießling and the JMU Chair of Experimental Physics III. Additional contributions and ideas have been brought forward by Professor Alexander Szameit from the University of Rostock. JMU Physicists cooperate with Szameit's team on the topic of topological photonics within the cluster of excellence ct.qmat.
In order to demonstrate the non-Hermitian skin effect experimentally, the JMU team has used electric circuits with periodically arranged elements. Due to their resemblance to the crystal structure of a solid, such artificially arranged experimental settings are classified as a metamaterial.
Applications of topological matter in sight
Prospectively, the research team wants to investigate the interplay between topological states and non-Hermitian physics further. One key question will be to which extent the topological protection of states remains intact when interactions with the environment are present.
In the long term, the team intends to progress towards quantum hybrid circuits in which they plan to embed superconducting or other quantum mechanical circuit elements. Such circuits offer a versatile platform for the discovery of novel phenomena.
„We aim to transfer the insights from topological circuits to other metamaterial platforms in the pursuit of potential applications“, Professor Thomale sums up. This includes optical setups such as photonic waveguides. There, topologically protected states in non-Hermitian systems could prove relevant in the enhancement of signal processing and detectors as well as in the construction of a photonic quantum computer. Eventually, the ultimate scheme in the research on topological metamaterials is the reconnection of novel effects to actual solid states.
Sponsors
The work described was financially supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) in the Collaborative Research Center SFB-1170 Tocotronics and within the Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat (Würzburg-Dresden).
Prof. Dr. Ronny Thomale, Chair of Theoretical Physics I, University of Würzburg, T +49 931 31-86225, ronny.thomale@physik.uni-wuerzburg.de
Generalized bulk-boundary correspondence in non-Hermitian topolectrical circuits. Tobias Helbig, Tobias Hofmann, Stefan Imhof, Mohamed Abdelghany, Tobias Kiessling, Laurens W. Molenkamp, Ching Hua Lee, Alexander Szameit, Martin Greiter, Ronny Thomale. Nature Physics, 1 June 2020, DOI: 10.1038/s41567-020-0922-9
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



