From milk protein, a plastic foam that gets better in a tough environment
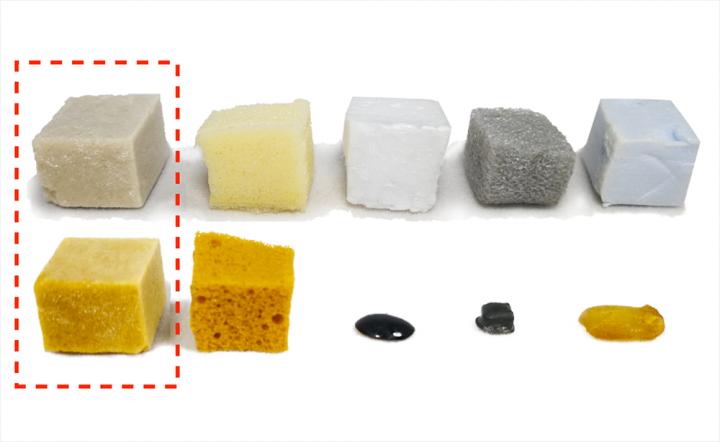
From left to right, foam materials consisting of whey, polyurethane, polystyrene, polyethylene and polystyrene. The top row represents unexposed materials and the bottom row represents the materials exposed to 150 degree air for one month.
Credit: KTH Royal Institute of Technology
A new high-performance plastic foam developed from whey proteins can withstand extreme heat better than many common thermoplastics made from petroleum. A research team in Sweden reports that the material, which may be used for example in catalysts for cars, fuel filters or packaging foam, actually improves its mechanical performance after days of exposure to high temperatures.
Reporting in Advanced Sustainable Systems, researchers from KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm say the research opens the door to using protein-based foam materials in potentially tough environments, such as filtration, thermal insulation and fluid absorption.
The basic building blocks of the material are protein nanofibrils, or PNFs, which are self-assembled from hydrolyzed whey proteins–a product from cheese-processing–under specific temperature and pH conditions.
In tests the foams improved with aging. After one month of exposure to a temperature of 150C, the material became stiffer, tougher and stronger, says the study’s co-author, Mikael Hedenqvist , professor in the Division of Polymeric Materials at KTH.
“This material only gets stronger with time,” he says. “If we compare with petroleum-based, commercial foam materials made of polyethylene and polystyrene, they melt instantly and decompose under the same harsh conditions.”
Proteins are often water-soluble, which poses a challenge when developing protein-based materials. Despite this, the material proved water-resistant after the aging process, which polymerized the protein, creating new covalent bonds that stabilized the foams. The foam also resisted even more aggressive substances–such as surfactants and reducing agents –that normally decompose or dissolve proteins. The crosslinking also made the foam unaffected by diesel fuel or hot oil.
The material also showed better fire resistance than commonly used polyurethane thermoset.
“This biodegradable, sustainable material can be a viable option for use in aggressive environments where fire resistance is important,” Hedenqvist says.
Potential applications include providing support for catalytic metals that operate at higher temperatures, such as platinum catalysts for automobiles. The material could conceivably work as a fuel filter, too.
Other possibilities are to use it as packaging foam and in applications for sound and thermal insulation where higher temperatures may occur and where there is a risk of an aggressive environment.
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



