Life’s rich pattern
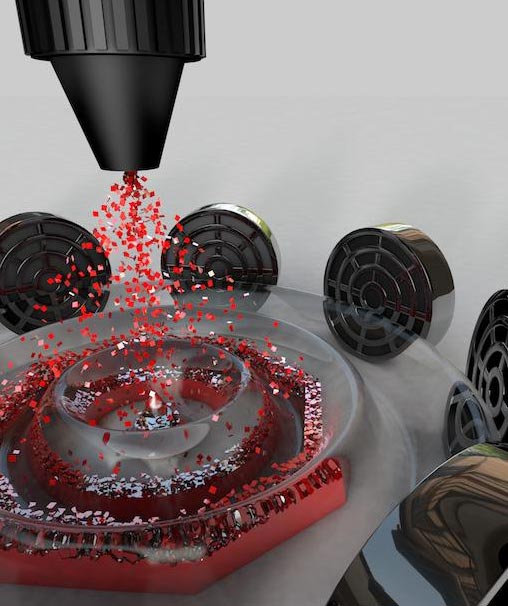
Utrasound and computer algorithms control how material settles into shape.
Credit: Universityies of Bath & Bristol
Researchers use sound to shape the future of printing.
Researchers in the UK have developed a way to coax microscopic particles and droplets into precise patterns by harnessing the power of sound in air. The implications for printing, especially in the fields of medicine and electronics, are far-reaching.
The scientists from the Universities of Bath and Bristol have shown that it’s possible to create precise, pre-determined patterns on surfaces from aerosol droplets or particles, using computer-controlled ultrasound. A paper describing the entirely new technique, called ‘sonolithography’, is published in Advanced Materials Technologies.
Professor Mike Fraser from the Department of Computer Science at the University of Bath, explained: “The power of ultrasound has already been shown to levitate small particles. We are excited to have hugely expanded the range of applications by patterning dense clouds of material in air at scale and being able to algorithmically control how the material settles into shapes.”
The researchers believe their work could revolutionise printing, improving the speed, cost, and precision of non-contact patterning techniques in air. Their work already shows the potential of sonolithography for biofabrication.
Dr Jenna Shapiro, research associate in the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at the University of Bristol and lead author of the article, said: “Sonolithography enables gentle, non-contact and rapid patterning of cells and biomaterials on surfaces. Tissue engineering can use biofabrication methods to build defined structures of cells and materials. We are adding a new technique to the biofabrication toolbox.”
Professor Bruce Drinkwater, professor of Ultrasonics in Bristol’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, added: “The objects we are manipulating are the size of water drops in clouds. It’s incredibly exciting to be able to move such small things with such fine control. This could allow us to direct aerosol sprays with unheard of precision, with applications such as drug delivery or wound healing.”
Beyond its applications in biomedicine, the team has shown the technique to be applicable to a variety of materials. Printed electronics is another area the team is keen to develop, with sonolithography being used to arrange conductive inks into circuits and components.
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



