Machine learning accelerates the discovery of new materials
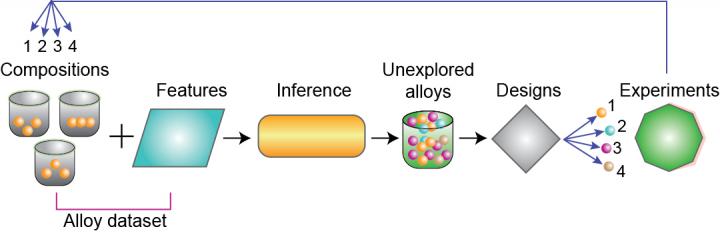
Feedback from experiments: augmented dataset with four new alloys. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory
Researchers recently demonstrated how an informatics-based adaptive design strategy, tightly coupled to experiments, can accelerate the discovery of new materials with targeted properties, according to a recent paper published in Nature Communications.
“What we've done is show that, starting with a relatively small data set of well-controlled experiments, it is possible to iteratively guide subsequent experiments toward finding the material with the desired target,” said Turab Lookman, a physicist and materials scientist in the Physics of Condensed Matter and Complex Systems group at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Lookman is the principal investigator of the research project.
“Finding new materials has traditionally been guided by intuition and trial and error,” said Lookman.”But with increasing chemical complexity, the combination possibilities become too large for trial-and-error approaches to be practical.”
To address this, Lookman, along with his colleagues at Los Alamos and the State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials in China, employed machine learning to speed up the process. It worked. They developed a framework that uses uncertainties to iteratively guide the next experiments to be performed in search of a shape-memory alloy with very low thermal hysteresis (or dissipation). Such alloys are critical for improving fatigue life in engineering applications.
“The goal is to cut in half the time and cost of bringing materials to market,” said Lookman. “What we have demonstrated is a data-driven framework built on the foundations of machine learning and design that can lead to discovering new materials with targeted properties much faster than before.” The work made use of Los Alamos' high-performance supercomputing resources.
Although the Materials Genome initiative, issued by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy in 2011, catalyzed interest in accelerated materials discovery, this study is one of the first to demonstrate how an informatics framework can actually lead to the discovery of new materials.
Much of the effort in the field has centered on generating and screening databases typically formed by running thousands of quantum mechanical calculations. However, the interplay of structural, chemical and microstructural degrees of freedom introduces enormous complexity, especially if defects, solid solutions, non-stoichiometry and multi-component compounds are involved, which the current state-of-the-art tools are not yet designed to handle. Moreover, few studies include any feedback to experiments or incorporate uncertainties.
Lookman and his colleagues focused on nickel-titanium-based shape-memory alloys, but the strategy can be used for any materials class (polymers, ceramics or nanomaterials) or target properties (e.g., dielectric response, piezoelectric coefficients and band gaps). This becomes important when experiments or calculations are costly and time-consuming. Although the work focused on the chemical exploration space, it can be readily adapted to optimize processing conditions when there are many “tuning knobs” controlling a figure of merit, as in advanced manufacturing applications. Similarly, it can be generalized to optimize multiple properties, such as, in the case of the nickel-titanium-based alloy, low dissipation as well as a transition temperature several degrees above room temperature.
###
The Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) program at Los Alamos funded the work and Los Alamos provided institutional computing resources. The researchers on the LDRD include a highly interdisciplinary team with post-docs Dezhen Xue, Prasanna Balachandran, Ghanshyam Pilania and staff scientists John Hogden, James Theiler, Jim Gubernatis, Kip Barros, Eli Ben-Naim, Quanxi Jia, Rohit Prasankumar and Turab Lookman.
The work supports the Lab's Nuclear Deterrence and Energy Security mission areas and the Information, Science, and Technology and Materials for the Future science pillars. Exploring the physics, chemistry and metallurgy of materials has been a primary focus of Los Alamos since its founding. Through the exploration of materials, Los Alamos pursues the discovery science and engineering required to establish design principles, synthesis pathways, and manufacturing processes for advanced and new materials to intentionally control functionality relevant to the Lab's national security mission.
Lookman and coauthors Dezhen Xue, Prasanna V. Balachandran, John Hogde, James Theiler, and Deqing Xue published their research in an article titled “Accelerated search for materials with targeted properties by adaptive design,” which was published in the April 15 issue of Nature Communications.
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, BWXT Government Group, and URS, an AECOM company, for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



