New self-cleaning membranes dramatically improve the efficiency of desalination technologies
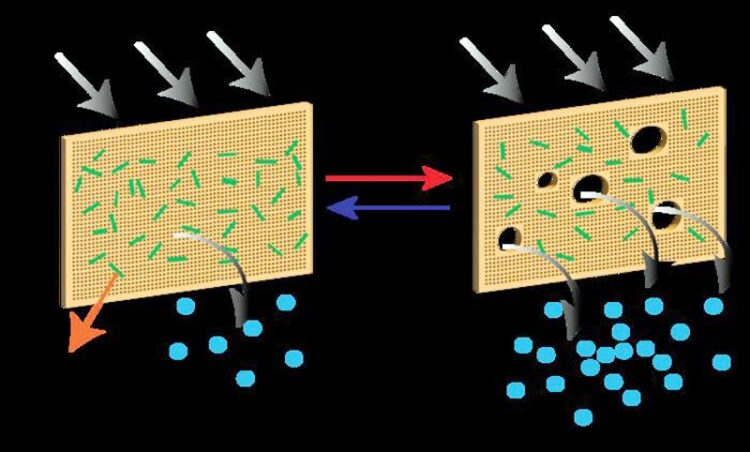
smart membrane function
Courtesy of NYU Abu Dhabi
Embedded with organic crystals, hybrid membranes use “smart separation” approach that is more effective and environmentally sustainable.
A team of NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) researchers has developed a new kind of self-cleaning, hybrid membrane that provides a solution that overcomes significant challenges that have, until now, limited desalination technologies.
The most energy-efficient desalination technologies are based on membrane desalination. However, the membranes used for desalination are prone to fouling, the accumulation of scale that results in decreased membrane performance, shorter lifespan, and the need for chemical cleaning, which has unknown environmental consequences.
Researchers at NYUAD’s Smart Materials Lab and the Center for Smart Engineering Materials, led by Professor Panče Naumov and Research Scientist Ejaz Ahmed, together with their collaborators from the Institute for Membrane Technology in Italy, created a unique hybrid membrane by utilizing stimuli-responsive materials, thermosalient organic crystals, embedded in polymers. The thermosalient crystals are a new class of dynamic materials that are capable of sudden expansion or motion upon heating or cooling.
Combining these microcrystals with traditional, porous membranes, the researchers developed a “smart” membrane capable of deformation by self-modulating its pore size and surface properties in response to changes in temperature. The crystals on the surface of the membrane respond to short-term increase in temperature, which activates the membrane to effectively remove the deposited contaminants from its surface. The researchers found that this “gating” process increased the flow of desalinated water by more than 43 percent through osmotic distillation and significantly extended the membrane’s operational lifetime.
The findings are presented in a paper titled Smart Dynamic Hybrid Membranes with Self-Cleaning Capability, published in the journal Nature Communications.
The ability of hybrid membranes to self-clean and minimize fouling could make desalination technologies more efficient and could increase the availability of freshwater. More than a third of the world’s population currently suffers from shortages of drinkable water, a number expected to reach 50 percent by 2025. In water-deficient countries, such as those in arid regions like the MENA region, membrane desalination of seawater helps coastal communities address local deficiencies.
“There is an urgent need for energy-efficient membranes capable of water desalination and other separation technologies that eliminate fouling issues without utilizing harsh chemicals as cleaners,” said Naumov. “The hybrid membrane we have developed demonstrates favorable consistency in performance after several cycles of descaling. With more than twenty types of dynamic organic crystals available to use with different membrane compositions, our novel approach represents an important step forward towards the development of a new generation of “smart” membranes that will be capable of self-cleaning in an energy-saving and environmentally benign manner, which will effectively improve the cost-effectiveness of the overall process of potable water production.”
This research is being carried out in the same period that NYUAD is chairing the Universities Climate Network (UCN). Comprising UAE-based universities and higher education institutions, the UCN collaborates on facilitating dialogues, workshops, public events, policy briefs, and youth participation in the lead up to and beyond COP28.
About NYU Abu Dhabi
www.nyuad.nyu.edu
NYU Abu Dhabi is the first comprehensive liberal arts and research campus in the Middle East to be operated abroad by a major American research university. NYU Abu Dhabi has integrated a highly selective program with majors in the sciences, engineering, social sciences, arts, and humanities with a world center for advanced research. Its campus enables students to succeed in an increasingly interdependent world, and to advance cooperation and progress on humanity’s shared challenges. NYU Abu Dhabi’s high-achieving students have come from some 120 countries and speak over 115 languages. Together, NYU’s campuses in New York, Abu Dhabi, and Shanghai form the backbone of a unique global university, giving faculty and students opportunities to experience varied learning environments and immersion in other cultures at one or more of the numerous study-abroad sites NYU maintains on six continents.
Journal: Nature Communications
Media Contact
Adam Pockriss
Rubenstein
apockriss@rubenstein.com
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



