To Make Stronger Platinum Jewelry, Add a Little Chromium
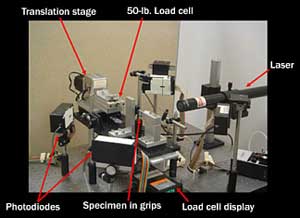
This lab setup enabled a Johns Hopkins undergraduate to test the mechanical properties of platinum alloys.
Student’s Testing Identifies Metal Mix with Superior Mechanical Properties
Using a high-tech but low-cost technique, a Johns Hopkins undergraduate has tested tiny samples of four metal alloys to find the best blend for use in platinum jewelry. After evaluating four metal mixtures, student researcher Christopher Kovalchick determined that platinum combined with a small amount of chromium in a cold-rolled and heat treatment process displayed the greatest strength.
The finding is important because pure platinum is too soft for use in a durable piece of jewelry. Yet many countries mandate that platinum jewelry must contain at least 95 percent of the precious metal by weight. With just 5 percent left to work with, jewelers are looking for the best platinum blend to produce strong and durable products. The mechanical properties of these alloys, such as hardness and elasticity, can also be altered through heat treatment and cold-rolling techniques.
Kovalchick’s testing method, pioneered by his faculty advisor, helped him keep costs low because it used ultra- thin samples, each smaller than a child’s thumbnail, rather than the large, expensive chunks required in conventional testing. The engineering mechanics major estimated that each platinum alloy microsample used in his tests cost $200. A traditional platinum-based test sample, measuring about 10 inches long, 1 inch wide and a half- inch thick, would cost nearly $50,000, the student said. “This is a very useful technique,” Kovalchick said. “It’s less expensive, but what we learn from the microsamples will also apply to larger amounts of the material.”
His presentation on platinum testing won first-place in the student competition at the annual conference of the Society for Experimental Mechanics, held recently in Portland, Ore. Kovalchick, a Hamilton, N.J., resident who will begin his senior year at Johns Hopkins in the fall, was the only undergraduate entrant, requiring him to compete against 17 graduate students.
His project began in March 2004, when Kovalchick asked William N. Sharpe Jr. to sponsor him in applying for an undergraduate research grant offered by the university. Sharpe, the university’s Alonzo G. Decker Professor of Mechanical Engineering, is an internationally recognized leader in microsample testing. The professor proposed a collaboration with the Centre for Materials Engineering at the University of Cape Town, South Africa, where researchers wanted an independent lab to test platinum alloys. South Africa is a leading source of platinum and boasts a growing platinum jewelry industry.
The Cape Town researchers sent 32 specimens of four alloys for testing by Kovalchick under Sharpe’s supervision. Each sample was only 200 to 400 microns thick, roughly three or four times the thickness of a human hair. For testing purposes, each was shaped like a tiny dog biscuit, about 3 centimeters long.
Each microsample was placed carefully between two grips. A motor pulled on one end, and a device called a 50-pound load cell measured the amount of force the sample withstood before breaking. The researchers also measured strain, the metal’s ability to stretch without breaking. This was done by a technique invented by Sharpe called interferometric strain/displacement gage. In this method, a laser is aimed at two small indentations in the metal specimen. The light bounces off the indentations, producing patterns that change as the metal is stretched. These changes, captured by photosensors, give the researchers data to measure the strain characteristics.
Kovalchick tested four alloys: a cold-rolled platinum blend containing 5 percent copper; a cold-rolled platinum blend containing 3.2 percent chromium; a 3.2 percent platinum-chromium blend that was cold-rolled and then heated to 300 degree Centigrade for three hours; and a 3.2 percent platinum-chromium blend that was recrystalized by heating it for six hours at 800 degrees Centigrade.
The student researcher determined that among these alloys, the platinum-chromium mix that underwent cold- rolling and three hours of heating displayed the greatest strength. The recrystalized alloy was the weakest. His detailed findings will be given to researchers in South Africa and are expected to be the focus of a scientific journal article.
“Because each microspecimen was a little different, this project turned out to be more involved and more complicated than we’d ever anticipated,” said Sharpe, Kovalchick’s faculty advisor. “But Chris finished the work, and he gave a fine presentation before the judges at the student competition.”
Kovalchick said he was well prepared because Sharpe and other Johns Hopkins engineering professors had grilled him with questions during a meeting before the science conference. “It was a great learning experience,” the student said. “This is what Hopkins prides itself on — giving undergraduates a chance to do research. This will give me a leg up when I go to grad school.”
His project was supported by a Provost’s Undergraduate Research Award from Johns Hopkins.
In addition to his engineering studies, Kovalchick is pursuing a second degree in violin performance at the Peabody Conservatory of Johns Hopkins. During his freshman and sophomore year, he was concertmaster of the Peabody Concert Orchestra. He is currently a principal in the Peabody Symphony Orchestra.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.jhu.eduAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



