Researchers use ultrasound waves to move objects hands-free
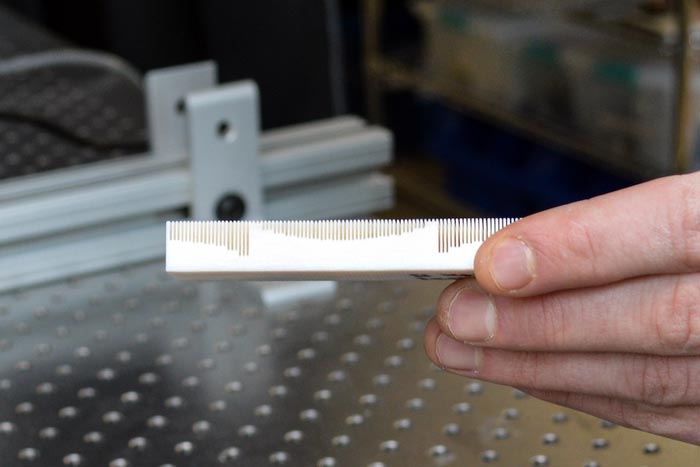
By placing a metamaterial pattern on the surface of an object, the University of Minnesota researchers were able to use sound to steer it in a certain direction without physically touching it.
Credit: Olivia Hultgren
Contactless manipulation method could be used in industries such as robotics and manufacturing.
University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers have discovered a new method to move objects using ultrasound waves. The research opens the door for using contactless manipulation in industries such as manufacturing and robotics, where devices wouldn’t need a built-in power source in order to move.
The study is published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed, open-access scientific journal.
While it’s been demonstrated before that light and sound waves can manipulate objects, the objects have always been smaller than the wavelength of sound or light, or on the order of millimeters to nanometers, respectively. The University of Minnesota team has developed a method that can move larger objects using the principles of metamaterial physics.
Metamaterials are materials that are artificially engineered to interact with waves, like light and sound. By placing a metamaterial pattern on the surface of an object, the researchers were able to use sound to steer it in a certain direction without physically touching it.
“We have known for a while that waves and light and sound can manipulate objects. What sets our research apart is that we can manipulate and trap much bigger objects if we make their surface a metamaterial surface, or a ‘metasurface,’” said Ognjen Ilic, senior author of the study and the Benjamin Mayhugh Assistant Professor in the University of Minnesota Department of Mechanical Engineering. “When we place these tiny patterns on the surface of the objects, we can basically reflect the sound in any direction we want. And in doing that, we can control the acoustic force that is exerted on an object.”
Using this technique, the researchers can not only move an object forward but also pull it toward a source—not too dissimilar from the tractor-beam technology in science fiction stories like Star Trek.
Their method could prove useful for moving objects in fields like manufacturing or robotics.
“Contactless manipulation is a hot area of research in optics and electromagnetism, but this research proposes another method for contactless actuation that offers advantages that other methods may not have,” said Matthew Stein, first author on the paper and a graduate student in the University of Minnesota Department of Mechanical Engineering. “Also, outside of the applications that this research enables, expanding upon our knowledge of physics is just a very exciting thing to do in general!”
While this study is more a demonstration of the concept, the researchers aim to test out higher frequencies of waves and different materials and object sizes in the future.
“In a lot of fields of science and engineering, robotics especially, there is the need to move things, to transfer a signal into some sort of controlled motion,” Ilic said. “Often this is done through physical tethers or having to carry some source of energy to be able to perform a task. I think we’re charting in a new direction here and showing that without physical contact, we can move objects, and that motion can be controlled simply by programming what is on the surface of that object. This gives us a new mechanism to contactlessly actuate things.”
This research was supported by the Minnesota Robotics Institute and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
In addition to Ilic and Stein, the research team included University of Minnesota Department of Mechanical Engineering undergraduate student Sam Keller and graduate student Yujie Luo.
Watch a video of the researchers moving an object with ultrasound.
Journal: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34207-7
Method of Research: Experimental study
Article Title: Shaping contactless radiation forces through anomalous acoustic scattering
Article Publication Date: 1-Nov-2022
Media Contact
Rhonda Zurn
University of Minnesota
rzurn@umn.edu
Office: 612-626-7959
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



