Seeing how grain boundaries transform in a metal
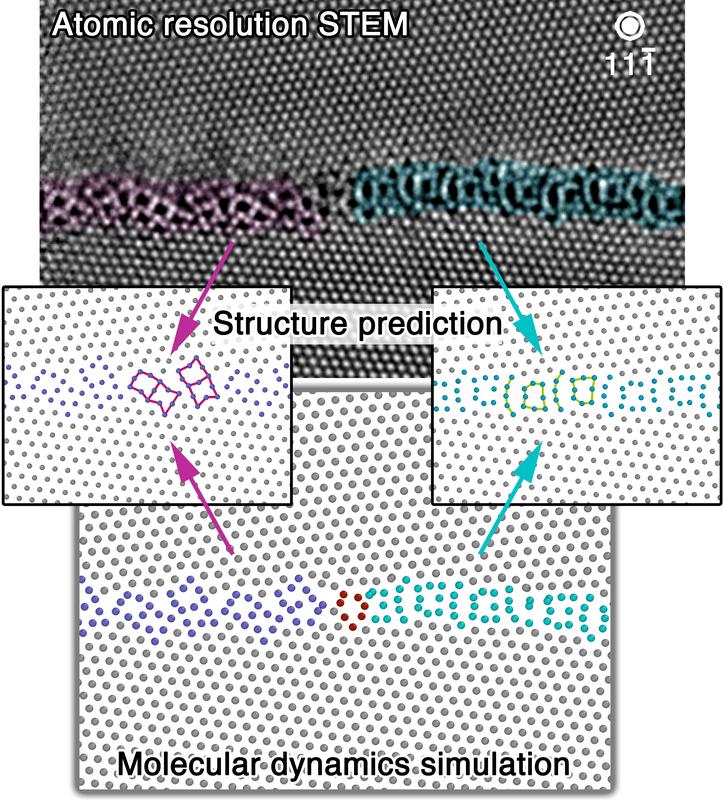
Atomic resolution STEM image of a grain boundary phase transformation in elemental Cu. Christian Liebscher, Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH
Grain boundaries are one of the most prominent defects in engineering materials separating different crystallites, which determine their strength, corrosion resistance and failure. Typically, these interfaces are regarded as quasi two-dimensional defects and controlling their properties remains one of the most challenging tasks in materials engineering.
However, more than 50 years ago the concept that grain boundaries can undergo phase transformations was established by thermodynamic concepts, but they have not been considered, since they could not be observed. Dr. Christian Liebscher, head of the group “Advanced Transmission Electron Microscopy” and his team members at the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung (MPIE), now found a way to directly observe grain boundary transitions experimentally.
With colleagues from the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), USA, who modelled the grain boundary transformations, the researchers published their recent findings in Nature.
Their results are surprising: “The search for congruent transformations has all the aspects of a search for a needle in a 6+C dimensional haystack.” This quote by John W. Cahn, material scientist and expert for thermodynamics, describes the complexity of experimentally proofing their existence and the team of MPIE and LLNL even found two of these “needles”.
The key was to utilize the atomic resolution microscopes at the MPIE to directly visualize the transforming interfaces. “We did not expect that we will see grain boundary phase transformations but our results clearly show that two grain boundary motifs coexist with different atomic arrangements. However, the grain boundary plane orientation, crystallite misorientation and chemical composition does not change.
Through these observations we have to re-think how interfaces behave while exposing a material to temperature and/or stress”, explains Liebscher. He and his colleagues analysed thin films of pure copper particularly by atomic resolved transmission electron microscopy. This way, they unlocked the grain boundary phases and proofed their coexistence with atomic precision.
The phases can be atomistically described as motifs with pearl and domino-shaped structure (see Fig. 1). Dr. Timofey Frolov and Dr. Robert Rudd, from the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, modelled the grain boundary phases. They used a novel grain boundary structure search algorithm, which is capable of finding the experimentally observed structures.
Moreover, their finite-temperature molecular dynamics simulations explore the transformation kinetics. The predicted structures not only perfectly resemble the experimental observations, but demonstrate that the grain boundary phases can transform into each other by changing temperature or stress. Additionally, the simulations indicate that the grain boundary phase junction, a novel line defect which has not been considered previously, is rate controlling.
“We discovered by modelling that the speed of the transformation largely depends on the migration of the phase junction. It takes only a few tens of nanoseconds in case of a short defect to complete the transformation from the domino to the pearl structure. Whereas no transformation is observed when the defect length exceeds a few nanometres and takes place below 500 K.”, explains Dr. Thorsten Meiners, first author of the publication and former doctoral researcher at the MPIE.
Furthermore, the grain boundary phases are characterized by different properties, which determine how the interface phases move, how they take up impurity elements or how they mechanically deform.
“Hence, understanding how grain boundaries transform provides a new view on still unexplained material phenomena, such as abnormal grain growth, and paves new ways to consider interface transitions as a material design element”, states Prof. Gerhard Dehm, director at the MPIE. The different states of grain boundaries or interfaces can have a strong impact on the corrosion behaviour of materials, how they behave under catalytic conditions or even play an important role in the failure of microelectronic devices.
The scientists aim to widen the current observations to experiments done at different temperatures, under stress and in the presence of impurities. The aim is to establish a complete understanding of these phase transformations, thus being able to design material properties by reaching out to a holistic grain boundary engineering. This research was mainly financed through the ERC Advanced Grant GB-CORRELATE (Grant Agreement 787446) of Prof. Gerhard Dehm.
Dr. Christian Liebscher, liebscher@mpie.de
T. Meiners, T. Frolov, R. E. Rudd, G. Dehm, C. H. Liebscher: Observations of grain boundary phase transformations in an elemental metal. In: Nature 579 (2020) 375–378. DOI 10.1038/s41586-020-2082-6
https://www.mpie.de/4249939/grain-boundary-phase-transformation-liebscher
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



