
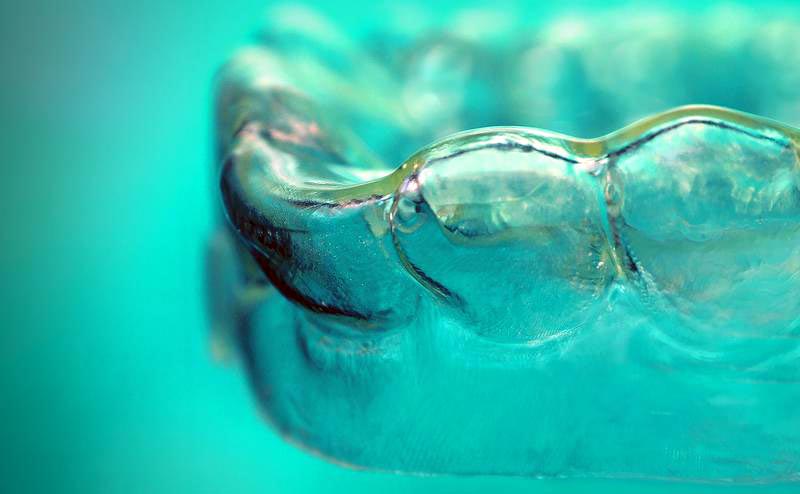
Aligners made of shape memory polymers can reduce the number of orthodontic splints in the therapeutic process.
(c) Fraunhofer IAP
… more sustainable, more cost-effective, gentler.
Clinically effective, custom-made, discreet and comfortable – the demands on aligners for the therapy of malocclusions are high. This also applies to the material of these orthodontic splints. A team at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research IAP in Potsdam, Germany, in cooperation with the University Hospital in Düsseldorf, Germany, has now developed a highly innovative material that enables completely new treatment concepts and reduces costs. The scientists focused on polymers with shape memory properties.
The novel material combines effective tooth movement with more efficient use of resources. “Aligners made of shape memory polymers allow to control the force acting on the teeth and thus make therapy more patient-friendly,” says Dr. Thorsten Pretsch, head of the research division “Synthesis and Polymer Technology” at Fraunhofer IAP, explaining the concept. “Our aligner allows several steps of tooth correction to be implemented at once,” Pretsch emphasizes. The advantages: Reducing the number of orthodontic aligners in the therapeutic process, avoiding excessive material waste and lowering treatment costs.
Memory effect for tooth correction
Shape memory polymers belong to the smart materials. Objects fabricated from these plastics can change their shape in a precisely predefined way. An external stimulus, such as heat, triggers the shape memory effect. The aligner slowly changes shape and thus moves misaligned teeth into the desired position.
Dual-effective aligner material
The head of the project at Fraunhofer IAP, M. Sc. Dennis Schönfeld, synthesized a thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) for the use in aligner therapy, which reacts to both heat and body-warm water. Depending on how high the temperature is or how much water the material absorbs, the change in shape of the aligner can be divided up into any number of individual steps. The results of a series of tests with denture models prove the functionality of the newly developed TPU: During thermal treatment, the team realized the movement of an incisor by a maximum of 3.5 millimeters. In addition, it was possible to gradually change the shape of the aligner within a specified period of time in water with body temperature. In the future, the shape memory effect could be triggered by saliva within the oral cavity. Thus, several correction steps could be realized with one splint. The clever choice of material thickness as well as the gradual heating of the aligner additionally controls the force applied to the teeth. “For orthodontic applications, these special features harbor a number of unique advantages in aligner therapy – from smaller shape adjustments through controlled heating to a reduction in the number of treatment steps,” Pretsch emphasizes.
Making aligner therapy sustainable
To date, aligners consist of materials that create strong compressive forces. Many small treatment steps are therefore required to correct a malocclusion without damaging the adjacent tissue. Each staging-step of the therapy requires a single removable, transparent aligner. Studies recommend limiting tooth movement to a maximum of 0.2 millimeters per aligner. The treatment with many individually manufactured splints thus incurs high costs. Depending on the degree of malocclusion, an average of thirty to sixty aligners have to be produced to move the teeth into the desired position over several months. The ability of the newly developed polymer to change shape in pre-determined, small and controlled steps has the potential to reduce the number of stages required in orthodontic treatment compared to therapies using conventional aligner materials.
Future technology for dental therapy
So far, the aligner material developed by the researchers at Fraunhofer IAP has been tested on model dental crowns. To optimize it for clinical application, the scientists focus on further material development. As a basis, the Polyclinic for Orthodontics at the University Hospital Düsseldorf conduct detailed biomechanical analyses. “Our investigations indicate that the newly developed material has a significantly higher efficiency, which means great advantages for orthodontic treatment,” reports Professor Drescher from the University Hospital Düsseldorf. The team is confident of transferring the novel technology to in vivo applications.
Funding
The project “Shape memory polymers for orthodontics” 20400 BG of the FGW Forschungsgemeinschaft Werkzeuge und Werkstoffe e. V. was funded by the Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Protection through the AiF Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen “Otto von Guericke” e.V. within the framework of the program for the promotion of joint industrial research (IGF) on the basis of a resolution of the German Bundestag.
Originalpublikation:
https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083094
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.iap.fraunhofer.de/en/press_releases/2023/smart-materials-for-aligner…















