Team tracks real-time molecular motions during singlet exciton fission
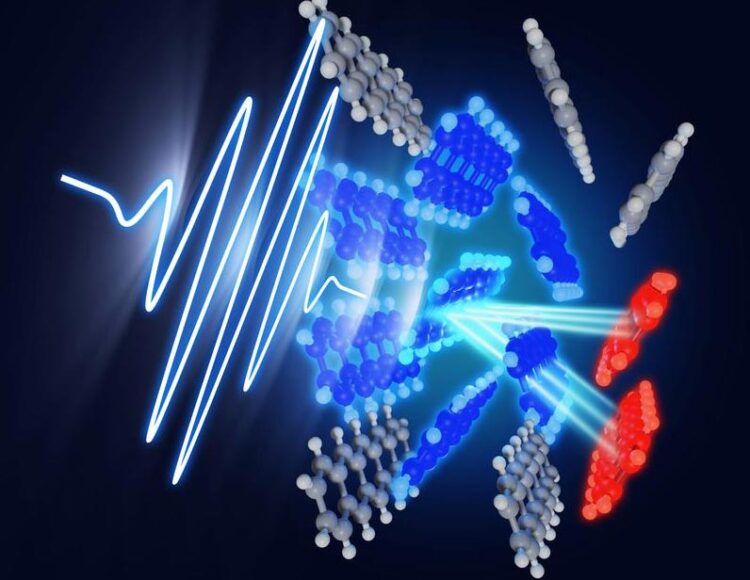
Während der Lichtabsorption wird ein Singulett-Exziton (blau) erzeugt, das sich dann auf ultraschnellen Zeitskalen in zwei Tripletts (rot) spaltet. Das Team verfolgte in Pentacen-Einzelkristallen in Echtzeit die begleitenden molekularen Bewegungen.
(c) Jörg Harms, MPSD
Researchers from the Fritz Haber Institute (FHI) in Berlin, the Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter (MPSD) in Hamburg and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg have provided important new insights into a key process for the development of more efficient solar cells and other light-based technologies, called singlet exciton fission. They have managed to track how molecules of a promising material, single crystals comprised of pentacene molecules, move in real time as singlet fission takes place, showing that a collective motion of molecules may be the origin of the fast timescales connected to this process.
Energy generation in light-based technologies relies on the ability of materials to convert light into electrical power and vice-versa. Certain organic molecular solids have the peculiar ability to significantly increase the solar to electrical power conversion efficiency, thanks to a process called singlet exciton fission (SEF). In this process two electron hole pairs, which are called excitons, are generated by the absorption of one light quantum (a photon). Because of the pronounced technological implications, it is no wonder that tremendous research efforts have been dedicated to understand how SEF really works.
The efficiency and speed of the SEF process are dictated by subtle details related to the way molecules arrange themselves in the material. Despite hundreds of studies on the topic, however, there had been no way to observe in real time how exactly the molecules move in order to facilitate the SEF event. Understanding this bit of the puzzle is essential to optimize SEF materials and further increase their efficiency.
In a study published today in Sciences Advances, researchers from the FHI, the MPSD and Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg have managed to track how molecules in a crystalline material build from pentacene molecules move during the SEF process, using an experimental technique called “femtosecond electron diffraction”. Such a technique can capture snapshots of the atomic structure in real-time as the SEF process unfolds. In order to be able to capture these snapshots in pentacene, a material which only contains small and light atoms, the measurements had to reach an exceptional stability and resolution.
“We have brought such experiments to a point where they can treat these materials, which is very exciting for chemistry, biology and materials science. These measurements have revealed that truly collective molecular motions accompany the SEF process in pentacene. Specifically, an ultrafast delocalized oscillation of pentacene molecules has been identified, which facilitates efficient energy and charge transfer across large distances”, says Heinrich Schwoerer from MPSD.
Thanks to state-of-the-art theory, the team could reveal the molecular motions involved in the initial excitation event and how these motions trigger more complex molecular motions involving many molecules of the crystal. “Our theory analysis could resolve very complex molecular motions. We could identify a dominant one that involves molecules sliding with respect to each other, and that can only be triggered through the coupling of electronic excitations to other more localized molecular motions, that then, in turn, couple to this key motion also observed in experiment ”, says Mariana Rossi from MPSD.
These collective atomic motions observed by the team involved in the project may well be the key to explain how the two excitons generated from the SEF process can separate, which is a prerequisite to harvest their charges in a solar energy device. “Simply put, our picture is that these molecular motions efficiently neutralize the forces that keep the two excitons together right after they have been generated, providing a possible explanation about the origin of the ultrafast timescales related to the fission, and thereby facilitate the high efficiency of solar to electrical energy conversion”, says Hélène Seiler, a postdoctoral fellow at the FHI in the group of Ralph Ernstorfer.
“Beyond providing important insights into the SEF process, this work shows that it is possible to reveal the atomic motion in more complex, functional organic materials, which are delicate and composed of light atoms,” concludes Sebastian Hammer from the University of Würzburg.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Hélène Seiler, lead author: seiler@fhi-berlin.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/7/26/eabg0869
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



