Biocompatible 3-D tracking system has potential to improve robot-assisted surgery
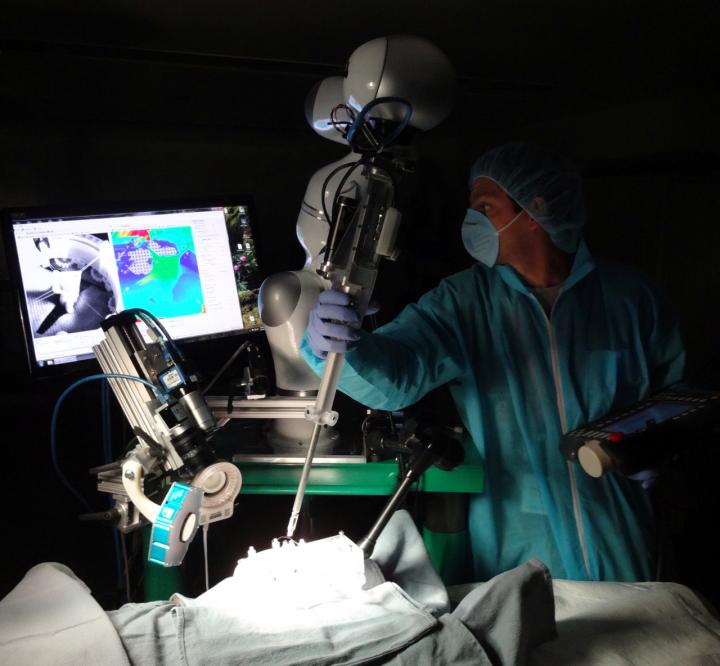
Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR), developed by the Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation at Children's National Health System, performed the first supervised autonomous robotic soft tissue surgery on a live subject in May 2016. Credit: The Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation at Children's National Health System
The study successfully demonstrates feasibility in live subjects (in-vivo) and demonstrates 3D tracking of tissue and surgical tools with millimeter accuracy in ex-vivo tests. More accurate and consistent suturing helps reduce leakage, which can improve surgical outcomes.
Authored by the development team from Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation at Children's National Health System and funded by the National Institutes of Health, the study explains the design of the 3D tracking system with near-infrared fluorescent (NIRF) markers and, using robotic experiments, compares its tracking accuracies against standard optical tracking methods. At speeds of 1 mm/second, the team observed tracking accuracies of 1.61 mm that degraded only to 1.71 mm when the markers were covered in blood and tissue.
“A fundamental challenge in soft-tissue surgery is that target tissue moves and deforms, becomes occluded by blood or other tissue, which makes it difficult to differentiate from surrounding tissue,” says Axel Krieger, Ph.D., senior author on the study and program lead for Smart Tools at the Sheikh Zayed Institute. “By enabling accurate tracking of tools and tissue in the surgical environment, this innovative work has the potential to improve many applications for manual and robot-assisted surgery.”
The system is made up of small biocompatible NIRF markers with a novel fused plenoptic and near-infrared (NIR) camera tracking system, enabling 3D tracking that can overcome blood and tissue occlusion in an uncontrolled, rapidly changing surgical environment. Krieger explains that the NIR imaging has the potential to overcome occlusion problems because NIR light penetrates deeper than visual light.
“This work describes the 'super human eyes' and a bit of 'intelligence' of our STAR robotic system, making tasks such as soft tissue surgery on live subjects possible,” explains Peter C. Kim, M.D., vice president and associate surgeon in chief of the Sheikh Zayed Institute.
Future work will include further integration and evaluation of the tracking system in image-guided medical interventions such as robotic surgeries.
###
The Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation at Children's National Health System is a hub for innovation focused on making pediatric surgery more precise, less invasive and pain free. It was founded in 2010 through a $150 million gift from the Government of Abu Dhabi. By combining research and clinical work in the areas of imaging, bioengineering, pain medicine, immunology and personalized medicine, the institute's physicians and scientists are developing leading-edge knowledge, tools and procedures that will benefit children globally.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Hyperspectral imaging lidar system achieves remote plastic identification
New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

SwRI awarded $26 million to develop NOAA magnetometers
SW-MAG data will help NOAA predict, mitigate the effects of space weather. NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recently awarded Southwest Research Institute a $26 million contract…

Protein that helps cancer cells dodge CAR T cell therapy
Discovery could lead to new treatments for blood cancer patients currently facing limited options. Scientists at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment…



