
New Imaging Analysis Transforms Head and Neck Tumor Diagnosis
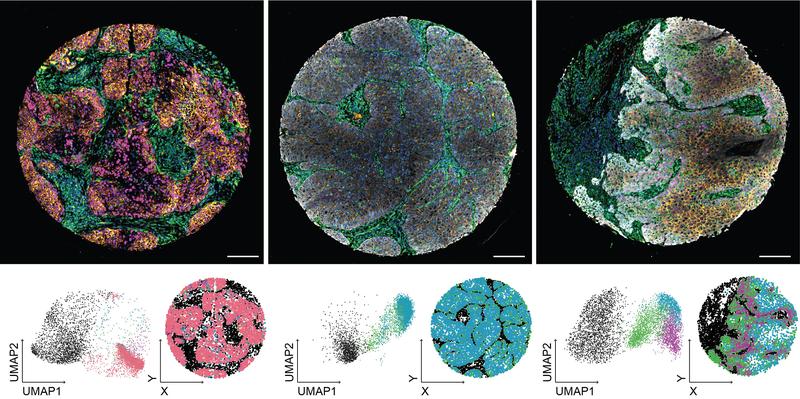
Patient biopsies were stained with fluorescent antibodies. The combination of morphological and cell-state markers allows a multiparametric description of each cell in the tissue.
(c) University Helsinki / Karolina Punovuori
… revolutionizes the diagnosis of head and neck tumors.
Head and neck cancers are among the ten most common cancers worldwide. Head and neck tumors account for about 3-5% of all cancers, with squamous cell carcinomas being the predominant form. They occur in areas such as the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx. An international team of researchers led by Sara Wickström has now developed a new technique that allows the properties of cancer cells and their surrounding tissue to be analyzed in detail at the single-cell level. This innovation enables a more comprehensive assessment of prognosis and therapy response in head and neck cancer and paves the way for a more precise diagnosis.
Head and neck cancers have increased significantly over the last 30 years. In Germany, there are about 18,000 to 20,000 new cases of head and neck tumors every year. In particular, the incidence of carcinomas of the middle pharynx has increased, which is associated with the increase in human papillomavirus (HPV) infections.
Using a machine-learning-based method, an interdisciplinary team of researchers led by Sara Wickström at the University of Helsinki, in collaboration with the University of Turku and the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Germany, analyzed hundreds of biobank patient samples at the level of individual cells. The new technology combines indicators of cancer cell behavior and the architecture of the tumor and surrounding healthy tissue to create a kind of ‘fingerprint’ for each patient that can be used to assess prognosis and response to cancer therapy.
The most important outcome of the study was the development of a new imaging method that combines the analysis of biomarkers of cell behavior with morphological analyses of the shape of individual cells and the structure of the entire tumor tissue. This method was able to identify two new, previously undiscovered patient groups: The first group had an exceptionally good prognosis, while the second had an exceptionally poor prognosis. The difference was explained by a specific combination of a particular cancer cell state and the composition of the tissue surrounding the cancer cells. In the second group, the aggressiveness of the disease was linked to the signaling between the cancer tissue and the surrounding healthy connective tissue, which is mediated by the epidermal growth factor (EGF).
‘These results are a breakthrough in our understanding of cancer development and diagnostics. For the first time, we have shown that certain combinations of malignant cells and tissue cell types in supposedly healthy tissue have a strong prognostic effect on the progression of cancer. Furthermore, we have identified a central signaling pathway that explains this combination effect and that can be pharmacologically targeted to significantly influence cancer progression,’ says principal investigator Sara Wickström. Sara Wickström was a professor at the University of Helsinki before becoming a director at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster until the end of 2021.
‘Furthermore, our method allowed us to identify patients with a particularly poor prognosis who would benefit from an aggressive treatment strategy. On the other hand, we also identified a group of patients with a good prognosis for whom less aggressive treatment, such as surgery alone, could be sufficient. This would help to maintain the patient’s quality of life,’ says Karolina Punovuori, first author of the study and postdoc in the University of Helsinki research group.
Diagnostic test in development
The new imaging method opens the door to precision diagnostics for cancers of the head and neck. The researchers are currently developing a diagnostic test for more accurate diagnosis of this type of cancer. In addition, they are also investigating the use of the method in the diagnosis of other types of cancer, such as colon cancer.
‘Our research uses the latest analytical methods in machine learning and spatial biology. We analyze hundreds of patient samples and millions of cells, which is only possible with the help of high-performance computing and artificial intelligence. This study is part of a new revolution in cancer diagnostics. We believe that the technology will significantly improve cancer diagnostics and the accuracy of treatment strategies,’ explains Sara Wickström.
‘Imaging of cancer biomarkers with antibody staining is already in clinical use. Therefore, the method will not be particularly expensive, as it only requires the algorithm we have developed and a special combination of antibodies. Considering the cost of cancer treatment, it is actually quite affordable,’ she continues.
About head and neck cancers
Although head and neck cancers are among the rarer cancers, they account for a significant proportion of cancers. Cancers of the head and neck have increased significantly over the last 30 years. In Germany, there are about 18,000 to 20,000 new cases of head and neck tumors every year. This accounts for about 3-5% of all cancers. Head and neck cancers include various malignant tumors that occur in areas such as the mouth, throat, larynx, nose, sinuses and salivary glands. An important risk factor is the consumption of tobacco and alcohol, which significantly increase the risk of these cancers. Infections with the human papillomavirus (HPV) are also playing an increasing role in certain cancers, such as throat cancer. The five-year survival rate for head and neck cancers is between 40% and 70%, with different subtypes having different prognoses.
Text: University Communications of University of Helsinki, MPI Münster
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Sara Wickström, Director
Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine
office-wickstrom@mpi-muenster.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
Multiparameter imaging reveals clinically relevant cancer cell – stroma interaction dynamics in head and neck cancer
Karolina Punovuori, Fabien Bertillot, Yekaterina A. Miroshnikova, Mirjam I. Binner, Satu-Marja Myllymäki, Gautier Follain, Kai Kruse, Johannes Routila, Teemu Huusko, Teijo Pellinen, Jaana Hagström, Noemi Kedei, Sami Ventelä, Antti Mäkitie, Johanna Ivaska, and Sara A. Wickström
Cell, Oct. 28, 2024, online ahead of print.
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.mpi-muenster.mpg.de/pressrelease/new-imaging-analysis-method-revolut…














