New technique to treating mitral valve diseases: First patient data
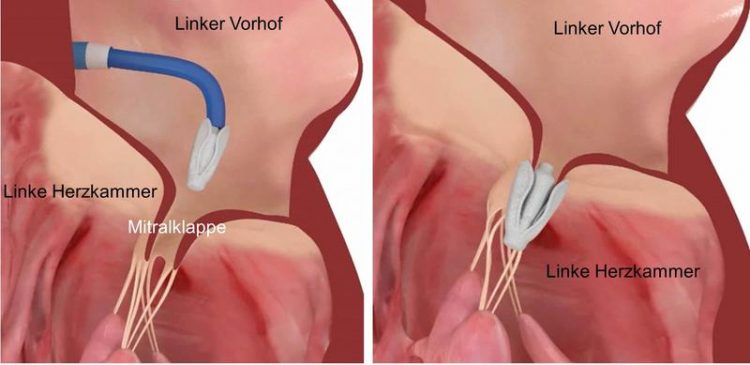
Starting from an inguinal vessel, the newly developed implant is introduced into the left atrium of the heart and placed at the site of the mitral valve leakage. Inselspital, Bern University Hospital
More and more people are fulfilling the wish for an active lifestyle into old age. But the societal trend is proceeding to the detriment of the heart, because use over the course of many years can render the mitral valve (the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle) leaky.
As a result, the heart has additional work due to the backlog of blood. Shortness of breath and ineffciency come about. Almost ten percent of the population over 75 years of age is affected. The development of safe and gentle treatment options for elderly patients with the shortest possible hospital stay is therefore a crucial challenge of contemporary cardiology.
When open heart surgery is out of the question
The optimal treatment of mitral valve diseases is still open heart surgery. But this major intervention poses a risk for many elderly patients because concomitant diseases often exist. As an alternative, the valve can be treated with a catheter through the groin in a minimally invasive (keyhole) procedure. Today cardiologists insert a clip here that repairs the leaking mitral valve. But the clip cannot be inserted with all patients, especially if the heart valve is severely altered.
A new American reconstruction system now has the potential to remedy this restriction. It also comes into question with such anatomically altered heart valves which could not be treated by means of catheter up to now. Cardiologists hope for a reduction in the number and duration of hospital stays and an improved quality of life for those affected.
First use at Bern University Hospital
The Departments of Cardiology and of Cardiovascular Surgery at Bern University Hospital are internationally renowned in the development of gentle and innovative treatment procedures for patients with heart valve diseases. Due to this reputation the new system was used for the first time worldwide in September 2016 at Inselspital, Bern University Hospital. Seven heart valve centres from five different countries (Germany, Greece, Canada, USA and Switzerland) subsequently verified the safety and feasibility of the procedure among elderly persons.
The evaluation of patient data under the leadership of Prof. Dr. med. Stephan Windecker at Bern University Hospital revealed that the new system can be used reliably among patients who were difficult to treat with available techniques. In addition, it closed the leaking mitral valve very effectively: 95 percent of patients indicated a noticeable improvement of their complaints after the procedure. These promising results will now be confirmed in long-term studies with a larger patient population before the new system can be approved. The initial evaluation was published on 19 August in “The Lancet”.
Contact:
Prof. Dr. med. Stephan Windecker, Director and Chief Physician, Department of Cardiology, Inselspital, Bern University Hospital, +41 31 63 2 44 97, Stephan.Windecker@insel.ch
http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)31600-8/fullte…
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.insel.chAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



