Seismic for the spine: Vibration technology offers alternative to MRI
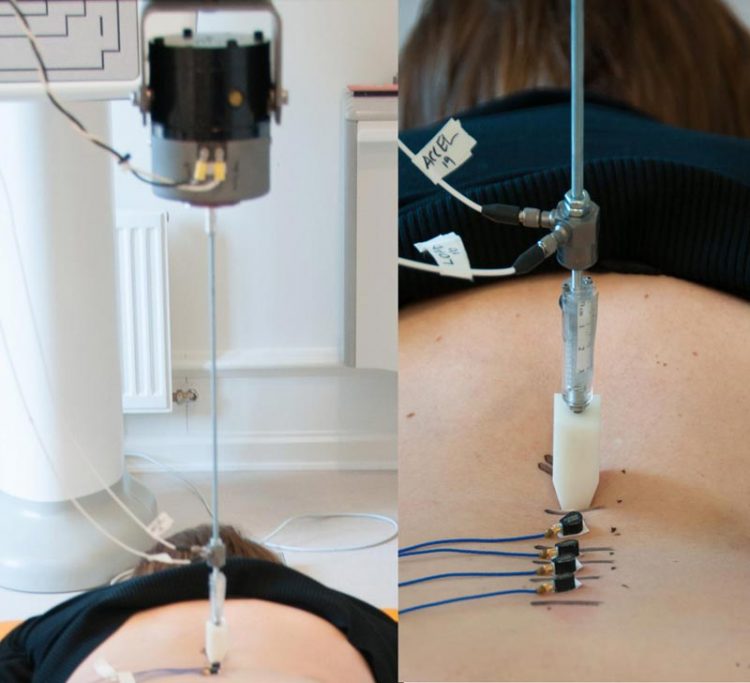
This image shows spine vibration technology at work on a patient's back. Credit: University of Alberta
Instead of using large seismic vibrations to find oil, we used gentle vibrations to find out where problems exist in the back,” explains Kawchuk, professor of physical therapy at the U of A's Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine. “By studying and testing vibration responses in identical twins, we were able to demonstrate that structural changes within the spine alter its vibration response.”
Publishing online in Scientific Reports on March 11, 2016, the identical twin study design is significant and unique for biomechanical studies like this one. In the instance where twins had similar spines, the vibration responses were statistically similar. Alternatively, if one twin had a different spine, due to an accident or injury for example, the vibration responses were significantly different from each other.
“In Denmark we have the world's largest and most comprehensive twin registry and using this unique resource, we have been able to contribute to research that can potentially help to diagnose millions of back pain patients,” says Jan Hartvigsen, professor of clinical biomechanics and musculoskeletal research, University of South Denmark.
The findings show the viability of vibration as a diagnostic tool that could help improve MRI utilization in the short term, Kawchuk says.
“One of the biggest problems in back pain today is over utilization of MRI scans in patients that do not need them. This is a waste of health care resources that leads to over treatment and even increased disability. By using a simple, safe and inexpensive technology like this, we can potentially decrease the use of these scans significantly,” says Hartvigsen.
The study also has implications in the long term and could provide new diagnoses not seen by current imaging tests.
“While an MRI shows us a picture of the spine, it doesn't show how the spine is working. It's like taking a picture of a car to see if the car is capable of starting. Vibration diagnostics shows us more than how the spine looks, it shows us how the spine is functioning,” explains Kawchuk.
“Back problems are a significant cause of disability world-wide. For 90 per cent of these patients, current diagnostic methods are not able to identify their problems,” says Cameron Schuler, President and CEO, VibeDxTM, who co-founded the VibeDx Diagnostic Corp, a TEC Edmonton spinoff company that has licensed the technology developed by Kawchuk. “Our hope is VibeDx™ will help improve our ability to identify the cause of the patient's back problem, which will then assist clinicians in matching a patient to the best course of treatment for their specific situation.”
“VibeDx™ is a TEC Edmonton client and we're delighted to see international recognition for this innovative University of Alberta spinoff,” said Chris Lumb, CEO of TEC Edmonton, an accelerator for early stage technology companies. “VibeDx™ is a prime example of the outstanding research and commercialization taking place in Edmonton and at the University of Alberta.”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



