Using sound and bubbles to make bandages stickier and longer lasting
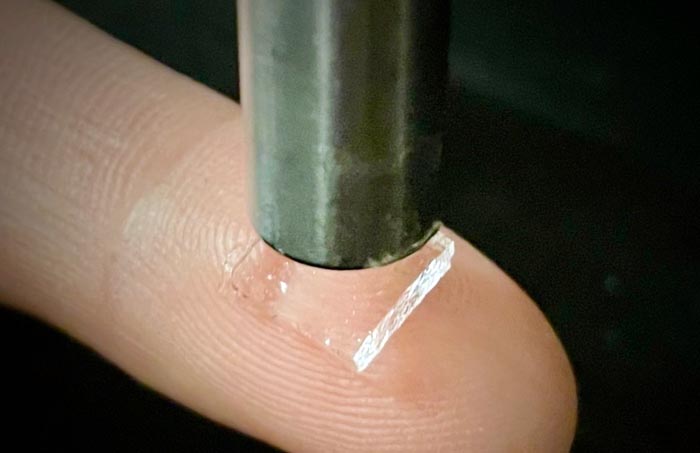
Adhesive hydrogel applied on skin under ultrasound probe.
Credit: Ran Huo and Jianyu Li
The stickiness of medical adhesives can be controlled by ultrasound, researchers find.
Researchers have discovered that they can control the stickiness of adhesive bandages using ultrasound waves and bubbles. This breakthrough could lead to new advances in medical adhesives, especially in cases where adhesives are difficult to apply such as on wet skin.
“Bandages, glues, and stickers are common bioadhesives that are used at home or in clinics. However, they don’t usually adhere well on wet skin. It’s also challenging to control where they are applied and the strength and duration of the formed adhesion,” says McGill University Professor Jianyu Li, who led the research team of engineers, physicists, chemists, and clinicians.
“We were surprised to find that by simply playing around with ultrasonic intensity, we can control very precisely the stickiness of adhesive bandages on many tissues,” says lead author Zhenwei Ma, a former student of Professor Li and now a Killam Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of British Columbia.
Ultrasound induced bubbles control stickiness
In collaboration with physicists Professor Outi Supponen and Claire Bourquard from the Institute of Fluid Dynamics at ETH Zurich, the team experimented with ultrasound induced microbubbles to make adhesives stickier. “The ultrasound induces many microbubbles, which transiently push the adhesives into the skin for stronger bioadhesion,” says Professor Supponen. “We can even use theoretical modeling to estimate exactly where the adhesion will happen.”
Their study, published in the journal Science, shows that the adhesives are compatible with living tissue in rats. The adhesives can also potentially be used to deliver drugs through the skin. “This paradigm-shifting technology will have great implications in many branches of medicine,” says University of British Columbia Professor Zu-hua Gao. “We’re very excited to translate this technology for applications in clinics for tissue repair, cancer therapy, and precision medicine.”
“By merging mechanics, materials and biomedical engineering, we envision the broad impact of our bioadhesive technology in wearable devices, wound management, and regenerative medicine,” says Professor Li, who is also a Canada Research Chair in Biomaterials and Musculoskeletal Health.
About this study
“Controlled tough bioadhesion mediated by ultrasound” by Jianyu Li et al. was published by Science.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abn8699
Journal: Science
DOI: 10.1126/science.abn8699
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Animal tissue samples
Article Title: Controlled tough bioadhesion mediated by ultrasound
Article Publication Date: 12-Aug-2022
Media Contact
Shirley Cardenas
McGill University
shirley.cardenas@mcgill.ca
Office: 514-398-6751
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



