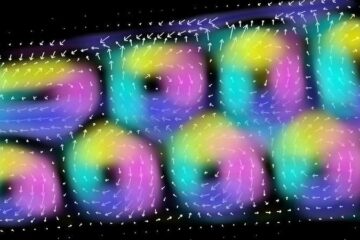
Dresden physicist wins prize for world’s first image of a 3D magnetic field. A Dresden research team led by solid-state physicist Dr. Axel Lubk has succeeded in imaging the magnetic…

During heavy storms, the normally stratified layers of water in ocean fjords get mixed, which leads to oxygenation of the fjord floor. But these storm events also result in a…

Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE, using a new antireflection coating, have successfully increased the efficiency of the best four-junction solar cell to date from 46.1…

Another success for Oldenburg’s hearing research: Collaborative Research Centre at the University of Oldenburg to receive funding for another four years. Smart hearing aids that adapt to the individual needs…

New carbon sorbent is 99% efficient, lightning fast, and easily recyclable. Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new carbon capture system which removes carbon dioxide directly from the…

… Just add CO2. Mount Erebus, Antarctica’s only active volcano, shows how carbon dioxide allows volcanoes to form persistent lava lakes at the surface. Antarctica has long been a land…

Curtin study. New Curtin University-led research has uncovered what may be the oldest direct evidence of ancient hot water activity on Mars, revealing the planet may have been habitable at…

An inaugural measurement of the neutron will help physicists learn about nucleon structure and spin. Protons and neutrons–known collectively as nucleons–are the building blocks of matter, but one of these…

A massive collision of galaxies sparked by one travelling at a scarcely-believable 2 million mph (3.2 million km/h) has been seen in unprecedented detail by one of Earth’s most powerful…

Working with week-old zebrafish larva, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues decoded how the connections formed by a network of neurons in the brainstem guide the fishes’ gaze. The…

…uncover key mechanisms related to cognitive function. Discovery suggests broad implications for giving brain a boost. While it’s well known that sleep enhances cognitive performance, the underlying neural mechanisms, particularly…

Protein design aims to create customized antibodies for therapies, biosensors for diagnostics, or enzymes for chemical reactions. An international research team has now developed a method for designing large new…

A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

KIT researchers produce metamaterial with different extension and compression properties than conventional materials. With this material, the working group headed by Professor Martin Wegener at KIT’s Institute of Applied Physics…

Most people think of coffee cups, bathroom tiles or flower pots when they hear the word “ceramic”. Not so Frank Clemens. For the research group leader in Empa’s Laboratory for…

New deep learning architecture enables higher efficiency. It is the computational processing of images that reveals the finest details of a sample placed under all kinds of different light microscopes….

Humans and animals move with remarkable economy without consciously thinking about it by utilizing the natural oscillation patterns of their bodies. A new tool developed by researchers at the Technical…

AI-enhanced metalenses achieve high-resolution, full-color imaging for compact optical systems. Modern imaging systems, such as those used in smartphones, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) devices, are constantly evolving…