Sloshing proteins help bacteria find their waists.
Chemical waves may help a bacterium to divide by pinpointing its middle, according to a new model of protein interactions 1 .
Bacteria such as Escherichia coli multiply by dividing. Bacterial division (called binary fission) is simpler than human cell division (mitosis). Human cells erect scaffolding to transport components to the two nascent daughter cells at either end; bacteria just pinch in two.

Chemists make the world’s smallest building blocks.
US researchers have made the world’s smallest building blocks. The nanocubes are just a millionth of a millimetre (a nanometre) across 1 . Stacked like bricks, they could make up a range of materials with useful properties such as light emission or electrical conduction.
Many chemists are currently trying to develop molecular-scale construction kits in which the individual components are single molecules to
When it comes to locating a meal, insect-eating bats generally employ one of two foraging tactics: capturing prey in the air or snatching it from a substrate. Accordingly, the animals use different kinds of echolocation during these activities. Whereas aerial hunters tend toward longer calls with constant frequency, substrate-gleaning species generate short calls that sweep from low to high frequencies (FM echolocation). Less clear, however, is how effective the latter is at distinguishing the prey i
Most climate change research has focused on gradual changes, such as the processes by which emissions of greenhouse gases lead to warming of the planet.
But new evidence shows that periods of gradual change in Earth’s past were punctuated by episodes of abrupt change, including temperature changes of about 10 degrees Celsius, or 18 degrees Fahrenheit, in only a decade in some places.
Severe floods and droughts also marked periods of abrupt change.
A new report from the Nati
An experiment that University of Chicago physicists conducted just for fun has unexpectedly led them to a new technique for producing nanoscale structures.
The Chicago physicists have built simple electronic devices using the new technique, which precisely controls the growth of metal wires along tiny scaffolds that automatically assemble themselves following nature’s own tendencies.
“This is perhaps the first time that it has been possible to assemble large numbers of parallel, contin
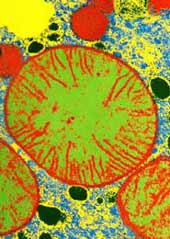
American Society for Cell Biology Meeting, Washington, December 2001
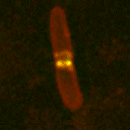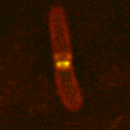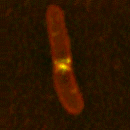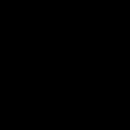
Microscope captures mitochondria bopping to a beat.
An intricate mesh of tubes wiggle, worm-like across the screen. “They’re speeding,” says Tim Richardson proudly, watching mitochondria, the cell’s energy generators, zoom around the cell. His controversial microscopic method is shooting the cell’s innards as they’ve never been seen before.
Live cell imaging has revolutionised cell biology over th