Researchers have discovered the mechanism by which the genetic defect underlying cystic fibrosis (CF) leads to fatal bacterial colonization of the lungs. The new findings, published today in the early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that an aerosol treatment aimed at balancing pH in lung cells could be developed to stave off or delay such infections.
The most common inherited lethal disorder in Caucasians, CF stems from mutations in a gene that
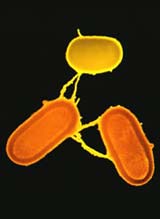
Bacteria caught mating with mammalian cells.
Cross-species coupling is generally frowned upon. But in the liberal labs of California it is actively being encouraged. Bugs that are persuaded to get down and dirty with hamster cells are rewriting sex manuals in the act.
Like humans, bacteria mate using a timely protruding phallus. It suckers a nearby bacterium and drags it close enough to shoot in DNA – a process called conjugation.
Although bacteria have been persuad

A gene may protect people against variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
People who lack a gene involved in immune responses may be three times more likely to suffer from variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), a new study suggests1. The result, if borne out in larger studies, could point researchers toward therapies for the incurable brain disease.
vCJD is thought to occur when people are exposed to misshapen prion proteins from cows with bovine spongiform encephalopathy – B

New catalyst means greener paper is not pulp fiction.
Pollution from paper production could be cut, say US chemists, with a new way of refining wood pulp 1 . But the process must go through the mill before it can convert industry.
During paper production, gluey wood component lignin is stripped out to leave stringy cellulose. The harsh chemicals used create environmental pollutants, such as toxic and long-lasting chlorinated compounds.
A new chemical
Scientists are finally beginning to understand how common genetic differences among individuals underlie differences in the structures that make up their brains. In the first attempt to actually map these variations, neurologist Paul Thompson and colleagues at the University of California at Los Angeles have discovered that brain structures related to cognitive ability and language seem to be under tight genetic control. The group’s findings, which could help explain how diseases like schizophre

A microelectronic sensor may alert doctors to bacterial hazards.
Smart bandages could soon alert doctors to the presence of certain bacteria in a wound by glowing different colours. Researchers in the United States have created a tiny device that emits faint light of two colours in response to two types of bug 1 .
Benjamin Miller, of the University of Rochester in New York State, and colleagues hope that a refined sensor might ultimately generate an instant an