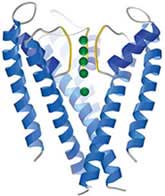
Dazzling snapshots show how ions power nerve signals round the body.
“Potassium channels underlie all our movements and thoughts,” says Rod MacKinnon of Rockefeller University in New York. His team has now unravelled the molecular mechanics of these minute protein pores. Some say the work merits a Nobel Prize.
Potassium (K + ) channels power the transmission of nerve signals through the body and the brain by ushering K + ions in and out of our cells. MacKin

Researchers have put a new face on what may be an old genetic weapon to help plants fight off a pesky infection. Abhaya Dandekar and colleagues at the University of California at Davis gave plants an extra gene that protected them from crown gall disease—a scourge of the walnut, grape and rose, among others—when tested in the lab. They publish their findings today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. When the bacterium that causes crown gall disease enters a plant, it starts

With a weather monitoring network a new model could predict coastal floods in Bangladesh. A new model should help forecast the massive floods to which the northern coast of Bangladesh is prone 1 . In principle, the model can predict the heights and arrival times of the huge waves that cyclones cause, and so could improve the planning of sea defences. The effectiveness of the model will depend on the availability of accurate, timely and detailed meteorological data, ca
Scientists have long noted that people suffering from Parkinson’s disease commonly exhibit a specific personality type characterized by, among other things, a lower-than-average tendency to seek out new experiences. In explanation, investigators suggested that this trait was rooted in an inability to reap the pleasurable rewards of increased dopamine levels normally brought about by new stimuli because the disease destroys the neurotransmitter. Previous studies of personality and dopamine activi

New light-sensitive glass can be recycled cleanly.
Researchers in Japan have developed recyclable light-sensitive glass. The new ’ecoglass’ does not contain the environmentally damaging halogen elements chlorine, bromine or iodine. These elements are essential to the photochromic glass that is currently used for car windscreens, sunglasses and visual display units.
Like photographic film, today’s photochromic glasses darken because they contain compounds of silver and halog
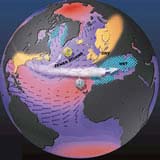
Ozone miniholes over the North Atlantic follow the unsteady pulse of climate fluctuations.
Recurring fluctuations in the North Atlantic climate are punching miniholes in the ozone layer, exposing Scandinavia and northern Europe to higher levels of ultraviolet radiation than normal, say two climatologists.
Seesawing air pressure over Greenland and the subtropical north Atlantic Ocean stirs the atmosphere and wafts ozone-depleted air towards populated high-latitude regions in