
With a weather monitoring network a new model could predict coastal floods in Bangladesh. A new model should help forecast the massive floods to which the northern coast of Bangladesh is prone 1 . In principle, the model can predict the heights and arrival times of the huge waves that cyclones cause, and so could improve the planning of sea defences. The effectiveness of the model will depend on the availability of accurate, timely and detailed meteorological data, ca
Scientists have long noted that people suffering from Parkinson’s disease commonly exhibit a specific personality type characterized by, among other things, a lower-than-average tendency to seek out new experiences. In explanation, investigators suggested that this trait was rooted in an inability to reap the pleasurable rewards of increased dopamine levels normally brought about by new stimuli because the disease destroys the neurotransmitter. Previous studies of personality and dopamine activi

New light-sensitive glass can be recycled cleanly.
Researchers in Japan have developed recyclable light-sensitive glass. The new ’ecoglass’ does not contain the environmentally damaging halogen elements chlorine, bromine or iodine. These elements are essential to the photochromic glass that is currently used for car windscreens, sunglasses and visual display units.
Like photographic film, today’s photochromic glasses darken because they contain compounds of silver and halog
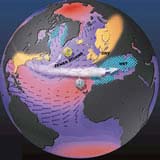
Ozone miniholes over the North Atlantic follow the unsteady pulse of climate fluctuations.
Recurring fluctuations in the North Atlantic climate are punching miniholes in the ozone layer, exposing Scandinavia and northern Europe to higher levels of ultraviolet radiation than normal, say two climatologists.
Seesawing air pressure over Greenland and the subtropical north Atlantic Ocean stirs the atmosphere and wafts ozone-depleted air towards populated high-latitude regions in
Recent events have confirmed that bioterrorism is no longer a threat but a reality. To provide wide-ranging access to the latest scientific information about anthrax and other potential bioweapons, Nature has put together a special online focus on this issue. This focus includes the pre-publication* of two research papers on anthrax toxin, as well as a collection of research, news and feature articles from our electronic archive. Because of the heightened interest in this area, among both the scient

Bugs behind typhoid and food poisoning give up genetic secrets.
Two teams have sequenced the genomes of two Salmonella bacteria. One is responsible for typhoid; the other causes food poisoning.
The genomes should lead to new ways to diagnose, treat and vaccinate against both diseases. Comparing the sequences should also clarify why the closely related bugs behave quite differently.
The two strains are called Typhi and Typhimurium. Typhi, the typhoid bug, infects onl