
Findings could drive new tissue engineering applications, organ repair and high-strength materials
Tufts University bioengineers have discovered how spiders and silkworms are able to spin webs and cocoons made of incredibly strong fibers. The answer lies in how they control the silk protein solubility and structural organization in their glands.
“This finding could lead to the development of processing methods resulting in new high-strength and high-performance materials use

You need to have thought of almost every eventuality when landing on a distant moon in a remote corner of the Solar System. You must have tested your spacecraft to its limits to be sure it will withstand the extreme conditions expected on Titan, a moon of Saturn.
Moreover, you have to gather in advance as much information as you can about the way your instruments will work in those conditions. It is only when the scientific instruments work properly that you can say your mission has been suc

Researchers see how robots respond in real-world rescue operations with FEMA’s Indiana Task Force 1 An earthquake has just laid waste to a small town. Major roads are impassable, and downed trees have cut power. Worse yet, the local library collapsed during the sudden temblor, trapping a half-dozen patrons. The robots are rushed in to help locate and free the survivors. That was the scenario facing a group of 14 researchers and a crew of search-and-rescue robots as they

The DC303.8-14.2 globule
A small and dark interstellar cloud with the rather cryptic name of DC303.8-14.2 is located in the inner part of the Milky Way galaxy. It is seen in the southern constellation Chamaeleon and consists of dust and gas. Astronomers classify it as a typical example of a “globule”.
As many other globules, this cloud is also giving birth to a star. Some years ago, observations in the infrared spectral region with the ESA IRAS satellite observatory detecte

September 1 is World Deafness Day
Deafness is a real and often underestimated health problem in Europe: 6% of the European population suffer of hearing impairment. It is now known that over 50% of all hearing impairments is caused by genetic factor. Over the last 7 years, the European Commission has channelled more than €10 million into research on different aspects of deafness. One particular project receiving support from the European Commission identified several genes which when
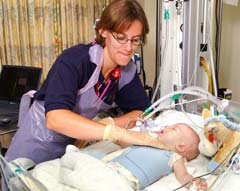
A new device being developed by researchers at the University of Southampton and Great Ormond Street Hospital is designed to optimise the effectiveness of chest physiotherapy techniques on babies and children suffering from breathing difficulties.
Rachael Gregson, a Research Fellow at the University’s School of Medicine and Great Ormond Street Hospital is leading the research and has developed an innovative sensing mat to measure chest physiotherapy.
Rachael says that although ches

NASA’s Coronal Diagnostic Experiment (CODEX) is ready to launch to the International Space Station to reveal new details about the solar wind including its origin and its evolution. Launching in…

In space exploration, long-distance optical links can now be used to transmit images, films and data from space probes to Earth using light. But in order for the signals to…

… in thunderstorm cloud-top corona discharges. A team of researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), led by Professors LEI Jiuhou, ZHU Baoyou, and Associate Professor…

Why tumors shrink but don’t disappear. “As tumors grow very quickly, consume a lot of oxygen and their vascular growth can’t necessarily keep pace, they often contain areas that are…

Researchers detail the inner workings of the most complex and intricate molecular machine in human biology. Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona have created the first…

By applying an electric field, the movement of microswimmers can be manipulated. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS), the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Hyderabad…

Takeout containers get your favorite noodles from the restaurant to your dining table (or couch) without incident, but they are nearly impossible to recycle if they are made from foil-lined…

Singlet fission can be promoted by chiral molecular self-assemblies that absorb light. In organic molecules an exciton is a particle bound pair of an electron (negative charge) and its hole…

Small drops, big impact: Over time, rain can damage the surfaces of rotor blades. This reduces the efficiency and profitability of wind turbines, especially at sea. Researchers from institutions of…

TU researchers enable better protection for sending sensitive information. In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the privacy of online communications is more critical than ever, especially in professions that rely on…

Researchers discover new magnetic and electronic properties in kagome magnet thin films. A discovery by Rice University physicists and collaborators is unlocking a new understanding of magnetism and electronic interactions…

– Wireless Aggregation of Health Data. Health data, distributed across various applications, could be unified in a digital medical twin: This is how doctors could improve patient care with the…