Reprogammable microarrays
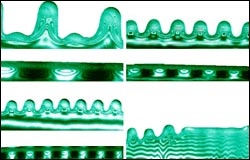
Physicists at the Georgia Institute of Technology have demonstrated a new optical technique for controlling the flow of very small volumes of fluids over solid surfaces. The technique, which relies on changes in surface tension prompted by optically-generated thermal gradients, could provide the foundation for a new generation of dynamically reprogrammable microfluidic devices.
A paper describing the technique is the cover story for the August 1 iss

Classification of quantum phenomena critical to high-temp superconductivity
A team of physicists led by researchers at Rice University has developed the first thermodynamic method for systematically classifying quantum phase transitions, mysterious electromagnetic transformations that are widely believed to play a critical role in high-temperature superconductivity.
The new research is described in two papers – one theoretical and one experimental – in the Aug. 8 issue of Phy
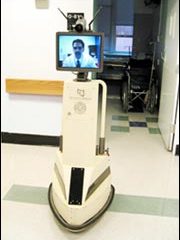
It lacks the warm bedside manner of Marcus Welby or Dr. Kildare, but a high-tech robot being tested at The Johns Hopkins Hospital could be used to link patients with their physicians in a whole new way.
Vaguely resembling a human torso, in a Star Wars R2D2 sort of way, the robot sports a computer screen for a head, a video camera for eyes and a speaker for a mouth. It walks, in a manner of speaking, on three balls, talks, and most importantly, listens. “That´s because the robot is directly
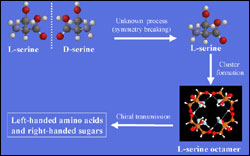
It may be a right-handed world, but recent Purdue University research indicates that the first building blocks of life were lefties – and suggests why, on a molecular level, all living things remain southpaws to this day.
In findings that may shed light on the earliest days of evolutionary history, R. Graham Cooks and a team of Purdue chemists have reported experiments that suggest why all 20 of the amino acids that comprise living things exhibit “left-handed chirality,” which refe

Why are elephants bigger than mice? The main reason is that mice have fewer cells. Research published in Journal of Biology this week uncovers a key pathway that controls the number of cells in an animal, thereby controlling its size.
Ernst Hafen and his colleagues from the University of Zürich used fruit flies to investigate the role of the insulin-signalling pathway and in particular a molecule called FOXO. If insulin signalling is reduced, for example by starving developing fly lar

How did life begin? What chemical combination launched the first organism with self-contained metabolism? And then what happened? Researchers in Robert H. White’s group at Virginia Tech are tracing the family tree of life on earth by tracing the biochemical mechanisms within the cell – specifically those that are used in the formation of peptide bonds.
The building blocks of enzymatic and functional structures in living organisms are proteins created by linking amino acids into pepti

In case you’re scratching your head, we help break it down. Using muon spin rotation at the Swiss Muon Source SmS, researchers at PSI have discovered that a quantum phenomenon…

In the 1997 movie “Contact,” adapted from Carl Sagan’s 1985 novel, the lead character scientist Ellie Arroway (played by actor Jodi Foster) takes a space-alien-built wormhole ride to the star…

NASA’s Coronal Diagnostic Experiment (CODEX) is ready to launch to the International Space Station to reveal new details about the solar wind including its origin and its evolution. Launching in…

A research group may have unraveled the mystery behind the locomotion of the ancient marine reptile, the plesiosaur, by recreating a bio-inspired control system that accounts for motion adjustment. Extinct…

Dysferlin protein protects and shapes the membrane of heart muscle cells. Researchers from the Heart Center of the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) led by Priv.-Doz. Dr Sören Brandenburg have…

There is fresh momentum in our protein supply — and it’s moving along on six legs. Insects are a source of protein with a smaller resource footprint than conventional alternatives…

Thermoplastic blends, produced by a new process, have better resilience. Now, experiments at the IRIS beamline show, why: nanocrystalline layers increase their performance. Bio-based thermoplastics are produced from renewable organic…

MXene nanomaterials enable wireless charging in textiles. Researchers demonstrate printed textile-based energy grid using MXene ink. The next step for fully integrated textile-based electronics to make their way from the…

Takeout containers get your favorite noodles from the restaurant to your dining table (or couch) without incident, but they are nearly impossible to recycle if they are made from foil-lined…

Researchers are perfecting processes to grow high-quality diamond material reliably and efficiently. Researchers are developing new ideas about the best ways to make lab-grown diamonds while minimizing other forms of…

TU researchers enable better protection for sending sensitive information. In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the privacy of online communications is more critical than ever, especially in professions that rely on…

Researchers discover new magnetic and electronic properties in kagome magnet thin films. A discovery by Rice University physicists and collaborators is unlocking a new understanding of magnetism and electronic interactions…