
Older adults with anemia are twice as likely to have a significant decline in physical performance that could threaten their independence, report researchers from Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center in the current issue of the American Journal of Medicine.
“Our results suggest that anemia is an independent risk factor for physical decline, which puts older adults at higher risk for nursing home admission, disability and death,” said Brenda Penninx, Ph.D., associate professor

In an article appearing in a special issue of the Journal of Neuro-oncology, researchers at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center’s Maxine Dunitz Neurosurgical Institute describe a complex cell-level process that allows malignant brain tumors to protect themselves by damaging the thymus, rapidly degrading the immune system. In a second article, Institute scientists identify a molecular mechanism that causes cell death of cancer-fighting lymphocytes as they infiltrate a brain tumor.
“We are
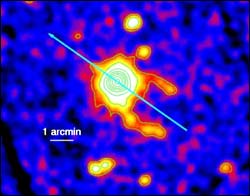
Astronomers using ESA’s X-ray observatory, XMM-Newton, have discovered a pair of X-ray tails, stretching 3 million million kilometres across the sky. They emanate from the mysterious neutron star known as Geminga. The discovery gives astronomers new insight into the extraordinary conditions around the neutron star.
A neutron star measures only 20-30 kilometres across and is the dense remnant of an exploded star. Geminga is one of the closest to Earth, at a distance of about 500 light-years.

Professor Lance Lanyon, Principal of The Royal Veterinary College, Karla Lee, Helen Jessop, Rosemary Suswillo, Gul Zaman from the Department of Basic Sciences at The Royal Veterinary College have shown in their research that the Estrogen Receptor has a fundamental role in bone cells by adjusting the bone architecture to match the loads individuals place on them. Their paper is published in the latest edition of Nature.
The strain imposed by mechanical loading on bone tissue normally stimulat

The scientist from the Institute of Plants and Animals Ecology, Russian Academy of Sciences (Ural Branch), has made a description of the giant dear remains, found in the Ural, and has determined their age. Giant deer Megaloceros giganteus originated as a species in the preglacial epoch, lived through the glaciation period and died out about 8-9 thousand years ago after the climate had become warmer. The remains will help to investigate how the giant dear lived and why this species disappeared. The r
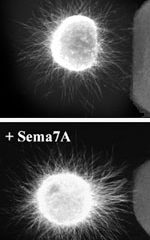
For decades, scientists have hunted for signals that guide nerve cells’ tentacle-like axons, hoping to understand how these cell tips reach out to distant targets. It’s knowledge that might one day help researchers learn how to rebuild nerves lost to spinal cord injuries or diseases like Huntington’s.
Now, a Johns Hopkins team studying a family of proteins best known for repelling axons and inhibiting their growth reports finding one member that unexpectedly promotes axon growth ins

In case you’re scratching your head, we help break it down. Using muon spin rotation at the Swiss Muon Source SmS, researchers at PSI have discovered that a quantum phenomenon…

In the 1997 movie “Contact,” adapted from Carl Sagan’s 1985 novel, the lead character scientist Ellie Arroway (played by actor Jodi Foster) takes a space-alien-built wormhole ride to the star…

NASA’s Coronal Diagnostic Experiment (CODEX) is ready to launch to the International Space Station to reveal new details about the solar wind including its origin and its evolution. Launching in…

A research group may have unraveled the mystery behind the locomotion of the ancient marine reptile, the plesiosaur, by recreating a bio-inspired control system that accounts for motion adjustment. Extinct…

Dysferlin protein protects and shapes the membrane of heart muscle cells. Researchers from the Heart Center of the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) led by Priv.-Doz. Dr Sören Brandenburg have…

There is fresh momentum in our protein supply — and it’s moving along on six legs. Insects are a source of protein with a smaller resource footprint than conventional alternatives…

Thermoplastic blends, produced by a new process, have better resilience. Now, experiments at the IRIS beamline show, why: nanocrystalline layers increase their performance. Bio-based thermoplastics are produced from renewable organic…

MXene nanomaterials enable wireless charging in textiles. Researchers demonstrate printed textile-based energy grid using MXene ink. The next step for fully integrated textile-based electronics to make their way from the…

Takeout containers get your favorite noodles from the restaurant to your dining table (or couch) without incident, but they are nearly impossible to recycle if they are made from foil-lined…

Researchers are perfecting processes to grow high-quality diamond material reliably and efficiently. Researchers are developing new ideas about the best ways to make lab-grown diamonds while minimizing other forms of…

TU researchers enable better protection for sending sensitive information. In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the privacy of online communications is more critical than ever, especially in professions that rely on…

Researchers discover new magnetic and electronic properties in kagome magnet thin films. A discovery by Rice University physicists and collaborators is unlocking a new understanding of magnetism and electronic interactions…