
Scientists often look to nature for inspiration in the search for ways to make new materials. A new study of the clamworm, an intertidal creature, shows that it has jaws made partly of zinc, making them strong, stiff and tough –– fundamental properties by which all materials are evaluated.
The properties of the clamworm jaws are described in this week´s online publication of the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences (PNAS). The research began with questions by scientists a

The search for life on other planets could soon extend to solar systems that are very different from our own, according to a new study by an Ohio State University astronomer and his colleagues.
In fact, finding a terrestrial planet in such a solar system would offer unique scientific opportunities to test evolution, said Andrew Gould, professor of astronomy here. In a recent issue of Astrophysical Journal Letters, he and his coauthors calculated that NASA’s upcoming Space Interferome

The promise of the genomics revolution – the ability to compare important genes and proteins from many different organisms – is that such detailed knowledge will produce new scientific insights that will improve human quality of life. In work on a key human enzyme, PBGS (porphobilinogen synthase), the laboratory of Fox Chase Cancer Center scientist Eileen K. Jaffe, Ph.D., has characterized a rare mutation that results in an unprecedented rearrangement of the enzyme´s structure. The discovery provides

Researchers of the Bochvara All-Russian Scientific Research Institute for Inorganic Materials, supported by the International Scientific and Technical Center have developed new tilth technology, which allows to get rid of radioactive or poisonous dust, to transform dust-forming slag-heaps into green lawn and even to grow forest in the desert.
The technology is based on the polyelectrolytes developed by chemists of the Lomonosov Moscow State University. The polyelectrolytes are polymers, the
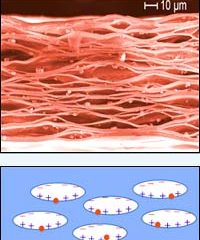
A research team in Austria has been unravelling the secrets of the charging of plastic foams. Its findings open the way for the development of flat microphones and loudspeakers, as well as “smart” surfaces that could be used as floor coverings, among other things. The interest in the success of the group´s work – which was co-funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) – has resulted in the integration of the project in a European interdisciplinary research network.
During a thunder st

The Liverpool Telescope, the world’s largest fully robotic telescope, has snapped its first images of the heavens this week. This 2 meter optical telescope is owned by the Astrophysics Research Institute (ARI) of Liverpool John Moores University (JMU), but observes autonomously from its site on La Palma in the Canary Islands. The telescope was designed, constructed and commissioned by Telescope Technologies Ltd., a subsidiary company of JMU.
The Liverpool Telescope’s unique capabilities of

Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, in collaboration with Chongqing University and the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, have achieved a breakthrough in topological…

Operations teams have confirmed NASA’s mission to “touch” the Sun survived its record-breaking closest approach to the solar surface on Dec. 24, 2024. Breaking its previous record by flying just…

At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger this anisotropy is, the better a…

HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…

Most solids expand as temperatures increase and shrink as they cool. Some materials do the opposite, expanding in the cold. Lithium titanium phosphate is one such substance and could provide…

Microorganisms are everywhere and have been influencing the Earth’s environment for over 3.5 billion years. Researchers from Germany, Austria and Taiwan have now deciphered the role they play in the…

Long gone are the days where all our data could fit on a two-megabyte floppy disk. In today’s information-based society, the increasing volume of information being handled demands that we…

In the search for new materials that can enable more efficient electronics, scientists are exploring so-called 2-D materials. These are sheets of just one atom thick, that may have all…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

Researchers from Osaka University introduced an innovative technology to lower power consumption for modern memory devices. Stepping up the Memory Game: Overcoming the Limitations of Traditional RAM Osaka, Japan –…

Cutting-Edge Framework for Enhancing System Security Researchers at the University of Electro-Communications have developed a groundbreaking framework for improving system security by analyzing business process logs. This framework focuses on…

AQSolotl’s quantum controller is designed to be adaptable, scalable and cost-efficient. Quantum technology jointly developed at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) and National University of Singapore (NUS) has now…