
An article published in the journal BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making describes the creation of the first comprehensive listing and classification of precancers, drawn from the medical literature. Using this classification, the precancers have been organized into groups that share similar biologic profiles and, hopefully, similar treatments.
Precancers precede invasive cancers. They are localized changes in tissue – lesions – identifiable by their morphologic structure. During car

One of the potential risks associated with the wider release of genetically modified crops and their use in mainstream agriculture is the hybridisation of transgenic plants with their wild relatives. Previous studies on mechanisms for the escape of transgenic material into the wild population have focused on pollen dispersal as the main route, but new work by scientists at the Université de Lille in France to be published in Proceedings B, a Royal Society journal, highlights the role of seed dispers

Using images from the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have concluded that two of the most common types of galaxies in the universe are in reality different versions of the same thing. In spite of their similar-sounding names, astronomers had long considered “dwarf elliptical” and “giant elliptical” galaxies to be distinct objects. The new findings, which appear in this month’s edition of The Astronomical Journal, fundamentally alter astronomers’ understanding of these important components of th

Scientists and computer gamers alike could benefit from a new method for creating soft, realistic shadows in computer-generated images.
Engineers at Ohio State University have created computer algorithms that model how light passes through translucent three-dimensional objects or fluids such as water, clouds, fire, and smoke. The result: shadows that begin to approach the realism of Hollywood animation, but don’t require as much computer memory to create.
Caixia Zhang, now a
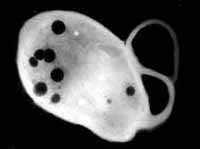
Researchers looking inside a pathogenic soil bacterium have found an organelle, a subcellular pouch, existing independently from the plasma membrane. The discovery within a prokaryotic organism challenges the theory on the origin of eukaryotic organelles and suggests a targeted approach to killing many disease-causing organisms.
“The organelle we found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is practically identical to the organelle called acidocalcisome in unicellular eukaryotes,” said R

Squealing brakes cost auto manufacturers several hundred million dollars a year in warranty repairs and are among consumers’ top 20 vehicle complaints – even in luxury cars. Now, acoustics researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed a solution that could stop the problem of noisy brakes once and for all.
In disc brakes, squeal can occur when the brake pads contact the rotor while the vehicle is moving at low speeds, setting up a vibration that manifests itself as an an

Operations teams have confirmed NASA’s mission to “touch” the Sun survived its record-breaking closest approach to the solar surface on Dec. 24, 2024. Breaking its previous record by flying just…

At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger this anisotropy is, the better a…

LSU quantum researchers uncover hidden quantum behaviors within classical light, which could make quantum technologies robust. Understanding the boundary between classical and quantum physics has long been a central question…

Exploiting an ingenious combination of photochemical (i.e., light-induced) reactions and self-assembly processes, a team led by Prof. Alberto Credi of the University of Bologna has succeeded in inserting a filiform…

A team led by plant biotechnologist Prof Markus Schwarzländer from the University of Münster and biochemist Prof Bruce Morgan from Saarland University has developed new biosensors with which the ratio…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Long gone are the days where all our data could fit on a two-megabyte floppy disk. In today’s information-based society, the increasing volume of information being handled demands that we…

In the search for new materials that can enable more efficient electronics, scientists are exploring so-called 2-D materials. These are sheets of just one atom thick, that may have all…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

AQSolotl’s quantum controller is designed to be adaptable, scalable and cost-efficient. Quantum technology jointly developed at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) and National University of Singapore (NUS) has now…

Pacific Northwest National Laboratory to contribute leadership to national effort in microelectronics design and development. Microelectronics run the modern world. Staying ahead of the development curve requires an investment that…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…