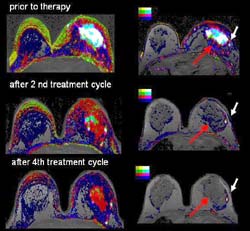
Scientists are using new imaging technology to help them perform “virtual biopsies,” – biological profiles of specific tumors that may help predict a patient’s response to treatment and probability of long-term survival. This whole new realm of imaging is called functional MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), a process that offers insight into a tumor’s character, not just its superficial structure.
Using functional MRI, Dr. Michael Knopp, a radiologist and a member of The Ohio State

A new approach to providing medication for adult diabetics (type 2 diabetes) that is not dependent on insulin has been developed by a doctoral student at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. For his work, which he did for his Ph.D. thesis in pharmacology, Arie Gruzman was awarded one of this year’s Kaye Innovation Awards at the Hebrew University.
Unlike other conventional drugs that require active insulin-producing cells in the pancreas and that often fail to overcome a companion problem of

The EU examines ways to reverse damage in the Mediterranean and Black Seas
Fifty years of intense development and exploitation have resulted in significant change to the fragile natural resources of the Mediterranean and Black Seas, and their coastal areas. Agreeing ways to prevent further environmental degradation will be the focus of the “International Conference on the Sustainable Development of the Mediterranean and Black Sea Environment” (IASON), to be held from 28 May to 1June i

Virologists at Jefferson Medical College may have discovered a new way by which HIV, the AIDS virus, can evade both anti-viral drugs and vaccines.
Researchers had reported last summer that a protein called CEM15 is a natural inhibitor of HIV, acting as a brake on HIV’s replication. They also showed that an HIV-encoded protein, Vif, or Virion infectivity factor, counteracts CEM15. Vif, in effect, is a shield to protect HIV from a host cell’s defenses.
But how CEM15 worked was somet

Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have begun unraveling the network of genes and proteins that regulate the lives of cells. The investigators compared the genome of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) to those of five other yeast species to identify all the locations at which molecules known as regulatory proteins attach to DNA to turn genes on and off. The study is published in the May 30 issue of the journal Science.
Among the many potenti

A new imaging technique that uses electron diffraction waves to improve both image resolution and sensitivity to small structures has been developed by scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The technique works on the same principle as X-ray diffraction, but can record structure from a single nanostructure or macromolecule.
Determining the structure of materials — such as protein crystals — is currently performed using X-ray diffraction. However, many small structur

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…