
China’s Three Gorges Dam, the largest dam project ever, has been seen by ecologists as an environmental disaster in the making. With construction scheduled to be completed later this year, little can be done to stop it, but some Chinese and American ecologists point out that the dark cloud of the environmental consequences does have a silver lining – an unprecedented opportunity to do environmental science.
In an article forthcoming in the May 23 issue of Science, Arizona State Univers
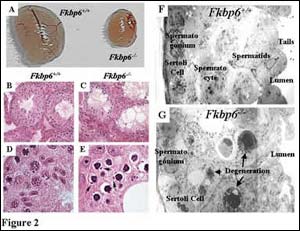
Mice without Fkbp6 gene have significantly reduced testes, completely lack sperm cells
A gene that belongs to a family of genes implicated in heart disease has been found to be essential for male fertility but has no impact on female fertility, researchers at U of T, along with colleagues in New York and Japan, have discovered.
“This gene – Fkbp6 – is a member of a family of genes that have been implicated in immunosuppression and heart disease,” says Dr. Josef Penninger, pr

As concerns rise about the ecological impacts of genetically modified crops, a new Indiana University study urges a pragmatic approach to dealing with “transgenes” that escape from crop plants into the wild. Use of transgenic crops is becoming more common as farmers reap benefits from the plants’ decreased susceptibility to disease and increased marketplace value.
IU biologist Loren Rieseberg and former postdoctoral fellow John Burke (now at Vanderbilt University) reported in the May 2

Niobium clusters display non-metallic properties at ultra-cold temperatures
The May 23 issue of the journal Science answers that question with an account of the surprising behavior exhibited by nanometer-scale clusters of the metal niobium. When the clusters are cooled to below 20 degrees Kelvin, electrical charges in them suddenly shift, creating structures known as dipoles.
“This is very strange, because no metal is supposed to be able to do this,” said Walter de Heer, a p

A crucial part in the battle to prevent outbreaks of deadly disease across the world lies with ecologists, an MSU professor says.
Preserving biodiversity and wildlife habitats are at the foundation of global health, says Jianguo “Jack” Liu, an ecologist who is the lead author for a Policy Forum in the May 23 issue of Science magazine.
The article outlines ways to protect biodiversity in China’s vast system of nature reserves. But Liu said the issues span farther than China, and

Butterfly flight simulator sheds light on epic migration
During their winter migration to Mexico, monarch butterflies depend on an internal clock to help them navigate in relation to the sun, scientists have found.
By studying monarchs inside a specially designed flight simulator, the researchers have gathered what they believe is the first direct evidence of the essential role of the circadian clock in celestial navigation. The study appears in the journal Science, publishe

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…