
Study identifies potential target for diabetes drugs
Researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have traced runaway sugar production in the liver – an important feature of diabetes – to flaws in a two-protein combination at the heart of a molecular switch that responds to insulin.
The findings, to be posted by the journal Nature on its Web site on May 18, suggest that drugs designed to block the interaction of the two switch proteins might be effective in treating diabetes,

MGH research suggests strategies for improving drug delivery to cancer cells
The best cancer drugs in the world are not much good if they cannot get to tumor cells. That problem has been challenging cancer physicians and researchers for years because the physical structure of many tumors can prevent anticancer agents from reaching their targets. In a study appearing in the June issue of Nature Medicine, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) describe a new technique for

Low-tech ‘Main Squeeze’ compresses for snug fit inside vehicle
Three Johns Hopkins University undergraduates have invented a low-tech tool that makes it much easier to properly install child safety seats in automobiles, ensuring a snug fit and maximum protection for the child.
The device, dubbed “Main Squeeze,” is intended to simplify the difficult task of compressing a child safety seat against a car’s permanent seat during installation. Incorrectly installed, a loose
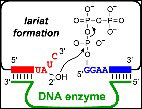
The production of lariat RNAs is a key step in the biologically important process of splicing. Because splicing changes the protein that is made from a given gene, a fundamental understanding of splicing is critical for comprehending the connections between genes and proteins. The study of splicing, however, has been very difficult in part because lariat RNAs have been nearly impossible to make artificially.
Now, chemistry professor Scott K. Silverman and graduate student Yangming Wang at th

A bacteria-killing virus found in the feces of some sheep could help remove the dangerous foodborne bacteria Escherichia coli O157:H7 from livestock. Researchers from Evergreen State College in Olympia, Washington present their research today at the 103rd General Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology.
“Here we report a promising new natural way of reducing pathogen concentrations in livestock. This takes advantage of bacteriophages – bacteria-killing viruses, harmless to humans a

A new anti-herpes agent derived from a common herb effectively treats and prevents the disease in animals. Researchers from Dalhousie University in Nova Scotia present their data today at the 103rd General Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology.
“Prunella vulgaris [also known as self-heal] is a perennial plant commonly found in China, the British Isles, Europe, and North America. In herbal literature, P. vulgaris has been described as a hot water infusion to treat sores in the mou

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…