
Researchers from Infineon Technologies AG have developed a way to make large textile surfaces such as carpeting or tent cloth “intelligent”. This technology innovation may lead to new products for the monitoring of buildings, the structural control of buildings of all kinds and for use in the advertising industry.
Woven into fabrics, a self-organizing network of robust chips is able to monitor temperatures, pressures or vibrations as required. In addition to the sensor functionality,
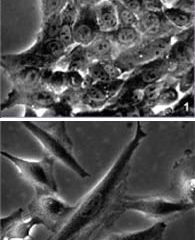
Although cells generally tend to “stay at home”, they may sometimes wish to take a look elsewhere, and this wandering has a whole range of consequences. During embryonic development, cells must migrate to give birth to new tissues. This roving spirit is essential to the modeling of the future living organism. In contrast, when tumor cells acquire the capacity to move around and invade other tissues, there is a risk that metastases will develop, thus rendering the treatment of cancer more difficult.

Pioneering research carried out by Kingston University is helping to pave the way for a manned mission to Mars. A project team based at the University’s School of Engineering has developed a robotic micro-rover to travel the Martian surface to find out whether humans could live in the Red Planet’s hostile environment.
Named Endurance, the small self-propelled vehicle will be powered by the sun’s rays and equipped to drill beneath the surface to find out if life exists on Mars in the form of
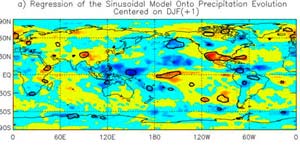
NASA-funded researchers have discovered El Niño’s soggy secret. When scientists identified rain patterns in the Pacific Ocean, they discovered the secret of how El Niño moves rainfall around the globe during the life of these periodic climate events when waters warm in the eastern Pacific Ocean.
The results may help scientists improve rainfall forecasts around the globe during the life of an El Niño, and may also offer new insights into how an El Niño develops.
The findings were hi

A new study by a University of Colorado at Boulder geological sciences professor suggests one earthquake causing up to 1 million fatalities on Earth each century could occur unless more earthquake-resistant construction materials are implemented.
Professor Roger Bilham’s conclusions are based on a study of the world’s urban population growth in the 21st century, including the number of rapidly expanding “supercities” and their locations close to major fault lines that have caused past tembl

The death of sensory hair cells when they try to multiply suggests need for caution in attempts to restore many kinds of lost cells through gene therapy
Researchers may have found a link between progressive hearing loss and a gene called p19Ink4d (Ink4d), according to results of a study that measured loss of hearing in mice lacking that gene. Normally, the Ink4d gene keeps healthy cells “quiet” – from inappropriately dividing.
Mice lacking the Ink4d gene become progressively

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…