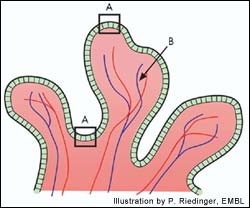
Researchers at EMBL and Harvard gain new insights into hemochromatosis
Like most nutrients, iron is good for people – in the right doses. When the body has enough iron, our cells stop absorbing it from food; if there is too little, they absorb more. This system breaks down in the most common inherited disease in the Western world: hemochromatosis, which affects about one in every 250 people and is often fatal if it is not recognized and treated. Now researchers at the European Molecu

The method that Staphylococcus aureus (staph) infection uses to inactivate the body’s immune response and cause previously healthy B cells to commit suicide, is described for the first time by researchers at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) School of Medicine in the May 5, 2003 issue of the Journal of Experimental Medicine. The paper was selected for early online publication on April 28.
Normally, B cells mount an early defense against invading bacteria. From this immunol

Insulin resistance, a condition commonly associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, is likely a major cause of heart disease in people with type 1 diabetes, according to study results published by University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health (GSPH) researchers in the May 2003 issue of Diabetes Care, a journal of the American Diabetes Association.
“Heart disease is a major complication for people with diabetes, including those with type 1 diabetes, and until now t

MENOPAUSAL WOMEN WITH DAYTIME SLEEPINESS SHOULD BE EVALUATED
Evaluation for sleep-disordered breathing should be a priority for menopausal women with complaints of snoring, daytime sleepiness, or unsatisfactory sleep. Researchers studied a population-based sample of 589 women enrolled in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study. They tested the hypothesis that menopause is an independent risk factor for sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) using in-laboratory sleep testing (polysomnography). (SDB is a

Drivers who are overweight or underweight are at greater risk of suffering an injury in a road accident than people of average size, according to a study of deaths and injuries from motor vehicle accidents in New Zealand.
The study appears in the current issue of the International Journal of Epidemiology (IJE), edited in the Department of Social Medicine at the University of Bristol.
Dr Gary Whitlock and colleagues studied people who had been seriously injured or killed betwe

A novel method for the design and manufacture of sensors to measure the temperature and relative humidity of the air, the pH of solutions or the refractive index of liquids based on optic fibre has been devised at the Public University of Navarre.
The sensors are small devices capable of capturing both physical and chemical signals from the surrounding environment and converting them into electrical signals for their subsequent processing. The information thus transformed can be easi

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…