
New data shows that the antiepileptic drug Keppra (levetiracetam), when used alone and in combination with other treatments, provided relief to more than 90 percent of patients with a range of pain syndromes, from migraine headaches to neck and back pain. The study of 400 patients, conducted by the Statesville Pain Associates of Statesville, N.C., was presented today at the American Pain Society’s 22nd Annual Scientific Meeting.
“To date, studies of Keppra to treat pain have been condu
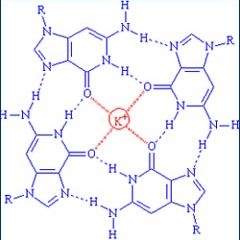
A team of investigators at Carnegie Mellon University has formed the first hybrid quadruplex of peptide nucleic acids, or PNAs, with DNA, the genetic code. This result opens new opportunities to study the activity of genetic regions occupied by recently described quadruplex DNA structures, as well as providing a new compound that could be used as a biosensor or to block gene activity associated with diseases such as cancer. The research results, published online, will appear in a forthcoming issue o

Cell phones, CD players and flashlights all wear down batteries far faster than we might wish. But there’s new hope, now that researchers at the Department of Energy’s Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory (INEEL) have overcome another barrier to building more powerful, longer-lasting lithium-based batteries.
The INEEL team, led by inorganic chemist Thomas Luther, discovered how lithium ions move through the flexible membrane that powers their patented rechargeab

Since the late 1970s, the amount of solar radiation the sun emits, during times of quiet sunspot activity, has increased by nearly .05 percent per decade, according to a NASA funded study.
“This trend is important because, if sustained over many decades, it could cause significant climate change,” said Richard Willson, a researcher affiliated with NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies and Columbia University’s Earth Institute, New York. He is the lead author of the study rece

Could yield biosensors with greater sensitivity, specificity
Scientists at Hebrew University, Israel, in collaboration with researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory, have devised a way to use gold nanoparticles as tiny electrical wires to plug enzymes into electrodes. The gold “nanoplugs” help align the molecules for optimal binding and provide a conductive pathway for the flow of electrons. The research, described in the March 21, 2003, issue of

Dutch technologists have carried out research into a more environmentally friendly car tyre. The scarcely mixable substances silica and rubber were mixed in a ratio that produced a tyre with a low rolling resistance and therefore a lower fuel use for the vehicle to which it will be fitted.
Louis Reuvekamp from the University of Twente mixed silica and rubber under the influence of organosilane. Tyre manufacturers normally use carbon black instead of silica to strengthen the rubber of car ty

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…