
May have potential value in treating patients with hematologic cancers
Researchers have developed a novel approach to genetically instruct human immune cells to recognize and kill cancer cells in a mouse model. The investigators plan to ultimately apply this strategy in a clinical trial setting for patients with certain forms of leukemias and lymphomas.
Scientists at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) genetically engineered an antigen receptor, introduced it into

An international research team, led by Dr. Erwin Schurr and Dr. Thomas Hudson, Scientists at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre, have identified a gene on human chromosome 6 that makes people vulnerable to leprosy. The study will be published in the March 2003 issue of Nature Genetics.
“This discovery will now allow us to study how the gene works and how it influences the infectious process. This is an important step toward the development of innovative prevention

A Duke University Medical Center neurobiologist has identified key mechanisms by which the intricate “protein machines” that govern the strength of connections among neurons build and remodel themselves to adjust those connections.
Such remodeling of the connections, called synapses, is central to the establishment of brain pathways during learning and memory, said the scientists. Also, malfunction of the synaptic machinery might well play a fundamental role in the pathology of neurodegenera

The technique that helped revolutionize modern biology by making the mouse a crucible of genetic manipulation and a window to human disease has been extended to human embryonic stem (ES) cells.
In a study published today (Feb. 10) in the online editions of the journal Nature Biotechnology, a team of scientists from the University of Wisconsin-Madison reports that it has developed methods for recombining segments of DNA within stem cells.
By bringing to bear the technique, known in
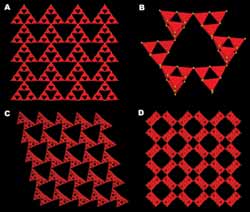
New materials will have applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices, electrocatalysis, electroanalysis and sensors
Scientists at the University of California, Riverside have synthesized a large family of semiconducting porous materials that have an unprecedented and diverse chemical composition.
The new materials show several different properties such as photoluminescence, ion exchange, and gas sorption. They also have a large surface area and uniform pore sizes. I

Scientists are studying water tables in the Southwest with an eye towards conservation
Scientists have discovered an unusual way to measure how fast water moves from the ground surface to the water table: they analyze the ground temperature.
Research in Vadose Zone Journal, published by the Soil Science Society of America, describes the methodology behind using temperature to analyze how much water is recharging the ground water at a specific location. The research describes

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…