
Groundbreaking research released on the economics of marine protected areas
For the first time anywhere, the analysis of leading economists and ecologists worldwide has been brought together in one place, to examine the economics of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs). Two special issues of the international research journal Natural Resource Modeling (Vol. 15 Nos. 3 &4) have just been published, within which the editors, Ussif Rashid Sumaila (University of British Columbia) and Anthony Char
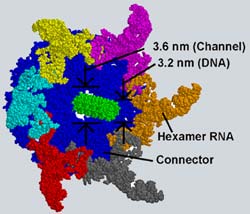
The Purdue University research team that recently created a tiny motor out of synthetic biological molecules has found further evidence that RNA molecules can perform physical work, a discovery that could advance nanotechnology and possibly solve fundamental mysteries about life itself.
Purdue’s Peixuan Guo has discovered how viral RNA molecules bind an energy-bearing organic molecule known as ATP. While linking these two substances might seem to create no more than a longer string of

In a new study in mice, a modified form of an innocuous chimpanzee virus has shown marked potency as a protective vaccine against HIV, itself believed to have crossed into the human population from chimpanzees sometime in the 1930s. The study, led by researchers at The Wistar Institute, appears in the February issue of the Journal of Immunology.
“Our results show this new vaccine is capable of inducing the kind of powerful immune response that we and others believe will be critical for cont

Research undertaken by Professor Einar Árnason at the University of Iceland, Reykjavik and published in the January 2003 issue of Annals of Human Genetics highlights the inaccuracy of claims that Icelanders are a ’genetically homogenous’ population.
Professor Árnason explains in his article: “Recently, statements have been made about a special ’genetic homogeneity’ of the Icelanders that are at variance with earlier work on blood groups and allozymes.” Iceland has been said to be an “islan

Scientists from The University of Manchester are playing a key role in a major Europe-wide study – believed to be the largest of its kind – of cancers of the mouth, pharynx and larynx (throat) and oesophagus (gullet). Incidences of these cancers are increasing faster in the UK than almost anywhere else in western Europe.
Every year, cancers of the upper aero-digestive tract kill approximately 10,000 in the UK alone. Alarmingly, these cancers are affecting younger people and are on the increa

Psychologists and human behaviorists are being enlisted by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in a pioneering new initiative to save the planet.
Experts believe that the traditional messages from governments and green groups, urging the public to adopt environmentally-friendly life-styles and purchasing habitats, need to be overhauled.
There is concern that many of these messages are too ‘guilt-laden’ and disapproving and instead of ‘turning people on’ to the env

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…