
Removing pituitary tumors through the nasal cavity rather than using the classic approach beneath the upper lip offers patients a minimally invasive alternative with similar results, less discomfort and faster recovery, a new UCLA study indicates.
The findings, published in the February 2003 edition of the peer-reviewed Journal of Neurosurgery, quantify the advantages of the direct endonasal approach over the sublabial procedure, regarded as the surgical standard for more than 40 years.

Just in time for Valentine’s Day, a report published in the February issue of the Journal of the American Dietetic Association says that chocolate is good for your heart.
Researchers at the University of California at Davis reviewed a number of recent studies on chocolate – particularly dark chocolate – and its health benefits. They found that flavan-3-ols, the main flavonoids found in cocoa, are associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease.
“Cocoa contains th

Some mice with a genetic mutation for mahogany-colored coats also develop spongiform degeneration of brain tissue, similar to mad cow disease. Because of this oddity, the mice could be valuable animal models for human disorders, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, according to geneticists at Cornell and Stanford universities.
The surprising discovery in a mouse strain known to geneticists since the 1960s is reported in the latest issue of the journal Science (Jan. 31, 2003

Researchers from Duke University Medical Center and the Medical College of Wisconsin have shown that removing a portion, instead of all, of the spleen, can successfully treat children with a variety of congenital anemias while preserving important splenic immune function.
In the largest study of its kind in the U.S., the researchers performed the surgery, known as a partial splenectomy, on 25 children with congenital forms of anemia caused by abnormal red blood cells. Typically, these

When 29-year-old Eric Lange suddenly experienced several hours of mental confusion last July, physicians at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center naturally ordered brain scans and carotid artery studies in their first search for a cause. With the initial exams turning out OK, Eric’s neurologist pursued other clues and ended up finding a heart defect called a patent foramen ovale, or PFO. A blood clot was believed to have slipped through the defect and out of the normal route of circulation that would
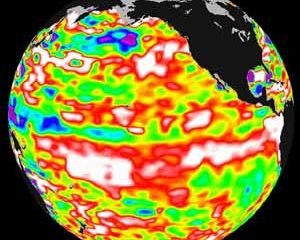
NASA sponsored scientists have discovered by knowing the salt content of the ocean’s surface, they may be able to improve the ability to predict El Nino events. Scientists, studying the western Pacific Ocean, find regional changes in the saltiness of surface ocean water correspond to changes in upper ocean heat content in the months preceding an El Nino event. Knowing the distribution of surface salinity may help predict events.
Salinity and temperature combine to dictate the ocean’s dens

At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger this anisotropy is, the better a…

LSU quantum researchers uncover hidden quantum behaviors within classical light, which could make quantum technologies robust. Understanding the boundary between classical and quantum physics has long been a central question…

One of the biggest mysteries in science – dark energy – doesn’t actually exist, according to researchers looking to solve the riddle of how the Universe is expanding. For the…

A team led by plant biotechnologist Prof Markus Schwarzländer from the University of Münster and biochemist Prof Bruce Morgan from Saarland University has developed new biosensors with which the ratio…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

Pacific Northwest National Laboratory to contribute leadership to national effort in microelectronics design and development. Microelectronics run the modern world. Staying ahead of the development curve requires an investment that…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…