
RNA interference (RNAi) has emerged as an extremely versatile and powerful tool in biomedical research. A new study published in the February issue of Nature Structural Biology reports the creation of transgenic mice in which inherited RNAi lowers or silences the expression of a target gene, producing a stable “gene knockdown.” This finding extends the power of RNAi to genetic studies in live animals, and has far-reaching implications for the study and treatment of many human diseases.
To a

Exposing rats to low levels of carbon monoxide prevents arteriosclerosis and chronic organ rejection
Exposing rats to low levels of carbon monoxide (CO) prior to aorta transplantation prevents arteriosclerosis associated with chronic organ rejection and can also suppress stenosis after balloon-angioplasty-induced carotid artery injury, according to a study published in the Feb. 1 edition of Nature Medicine. The article is published online today.
“These findings demonstrate a

Information could help identify at-risk individuals and estimate
Researchers at Rush-Presbyterian-St. Luke’s Medical Center have found evidence supporting a relationship between SIDS and the 5-HTT gene in both African-Americans and Caucasians. They found a significant positive association between SIDS and the L/L genotype, and between SIDS and the 5-HTT L allele, and a negative association between SIDS and the S/S genotype. This information might eventually lead to the identification

Fungus-growing ants practice agriculture and have been doing so for the past 50 million years according to research published in the Jan. 17 issue of Science. These ants not only grow fungus gardens underground for food but also have adapted to handling parasitic “weeds” that infect their crops.
The team of scientists who collaborated on this analysis includes Ted Schultz of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History, Bess Wong of the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, Came
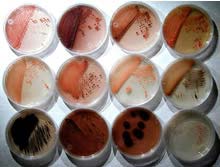
Promising cancer-fighting candidates emerge from tropical ocean ‘mud’
Although the oceans cover 70 percent of the planet’s surface, much of their biomedical potential has gone largely unexplored. Until now.
A group of researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego, have for the first time shown that sediments in the deep ocean are a significant biomedical resource for microbes that produce antibiotic molecules.
In a seri

Ground-breaking research at the University of Leicester into the division of chloroplasts holds out hope of a safer way of genetically modifying crops, with implications for agriculture particularly in the developing world.
Using three plant types – Arabidopsis, tomato and rice – Dr Simon Geir Møller has been working with colleagues in the University of Leicester Department of Biology and at the Laboratory of Plant Molecular Biology at the Rockefeller University in New York to examine how ch

At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger this anisotropy is, the better a…

LSU quantum researchers uncover hidden quantum behaviors within classical light, which could make quantum technologies robust. Understanding the boundary between classical and quantum physics has long been a central question…

One of the biggest mysteries in science – dark energy – doesn’t actually exist, according to researchers looking to solve the riddle of how the Universe is expanding. For the…

A team led by plant biotechnologist Prof Markus Schwarzländer from the University of Münster and biochemist Prof Bruce Morgan from Saarland University has developed new biosensors with which the ratio…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

Pacific Northwest National Laboratory to contribute leadership to national effort in microelectronics design and development. Microelectronics run the modern world. Staying ahead of the development curve requires an investment that…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…