
One and a half billion years ago the small, inconspicuous galaxy Messier 82 (M82) almost smashed into its large, massive neighbour galaxy Messier 81 (M81), causing a frenzy of star formation.
New research by astronomers from the Universities of Cambridge and Utrecht, Netherlands, has now discovered an elusive phenomenon in this violent “starburst” area. About 100 star clusters have been discovered that are believed to be the ancestors of the so-called “globular clusters” thought to be the ol

ESA’s Rosetta will be the first mission to orbit and land on a comet, one of the icy bodies that travel throughout the Solar System and develop a characteristic tail when they approach the Sun. Rosetta is scheduled to be launched on-board an Ariane-5 rocket in January 2003 from Kourou, French Guiana. A decision on the launch date will be taken by Tuesday 14 January (see Arianespace press release N° 03/02 of 7 January 2003 or at http:www.arianespace.com).
The mission’s target is Comet Wi

A vast, but previously unknown structure has been discovered around our own Milky Way galaxy by an international team of astronomers. The announcement is being made at the American Astronomical Society’s meeting in Seattle, Washington, on behalf of Drs Annette Ferguson, Rodrigo Ibata, Mike Irwin, Geraint Lewis and Nial Tanvir. Their observations suggest that there is a giant ring of several hundred million stars surrounding the main disk of the Milky Way. Despite its size, the ring has not been

University of Colorado at Boulder researchers have found, ironically, that two pollutants – carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons emitted from agricultural forest trees – offset each other somewhat in mitigating air quality problems.
Carbon dioxide, believed by scientists to be a major factor in greenhouse warming, has been shown to reduce “agriforest” emissions of hydrocarbons that contribute to ground-based ozone pollution, according to CU-Boulder doctoral candidate Todd Rosenstiel of the envir
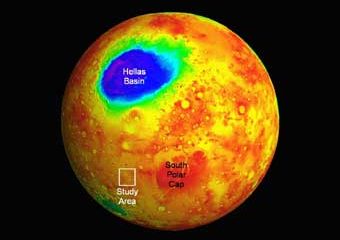
An Australian geologist has identified what could be the first ever active flow of fluids through gullies on Mars.
University of Melbourne geologist, Dr Nick Hoffman, identified recent gully and channel development near the polar regions of Mars from images taken by the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. But contrary to the majority of scientific opinion which suggests that such features were carved by liquid water, Hoffman says the flow is most likely frozen carbon dioxide.

This Chandra X-ray Observatory image of the supermassive black hole at the Milky Way’s center, a.k.a. Sagittarius A* or Sgr A*, was made from the longest X-ray exposure of that region to date. In addition to Sgr A* more than two thousand other X-ray sources were detected in the region, making this one of the richest fields ever observed.
During the two-week observation period, Sgr A* flared up in X-ray intensity half a dozen or more times. The cause of these outbursts is not understood

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…