
Researchers at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center’s Maxine Dunitz Neurosurgical Institute in Los Angeles have combined a special protein that targets cancer cells with neural stem cells (NSC) to track and attack malignant brain tumor cells. Results of their study appear in the Dec. 15 issue of Cancer Research.
Glioblastoma multiforme, or gliomas, are a particularly deadly type of brain tumor. They are highly invasive with poorly defined borders that intermingle with healthy brain tissue, maki

A collaboration of scientists from Harvard Medical School and Dartmouth Medical School has developed a new mouse model of lipoatrophic diabetes, and highlighted leptin therapy as a successful tool to combat this rare form of type II diabetes.
Lipoatrophic diabetes mellitus is characterized by a lack of subcutaneous fat (lipoatrophy), high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), and high blood insulin (hyperinsulinemia). Because patients with lipoatrophic diabetes are insulin-resistant, although high l

Dr. Mario Capecchi and colleagues at the University of Utah and the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center (Salt Lake City, UT) have discovered that a gene called xanthine oxidoreductase, or XOR for short, is required for lactation in female mice. This previously unidentified role for XOR in lactation reveals a possible genetic basis for the lactation difficulties experienced by nearly 5% of women.
XOR was originally identified as encoding an enzyme involved in purine catabolism (the

A key role in synchronizing daily rhythms to the day/night cycle has been traced to a light-sensitive protein in the eye, by knocking out the gene that codes for it. Mice lacking a gene for the photopigment melanopsin show a dramatic deficiency in their ability to regulate their circadian rhythms by light. The discovery, by National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) grantees, helps unravel the heretofore elusive mechanisms by which day/night cycles regulate such rhythms in mammals. NIMH grantees Igna
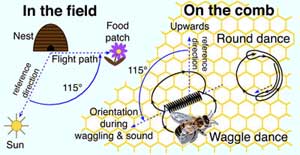
Honeybees communicate by dancing. The dances tell worker bees where to find nectar. A UC Riverside study reports that under natural foraging conditions the communication of distance and direction in the dance language can increase the food collection of honeybee colonies. The study also confirms that bees use this directional information in locating the food sources advertised in the dance.
Based on work done in 2001 in the Agricultural Experiment Station at UC Riverside, P. Kirk Visscher,

High-power ultrasound, currently used for cell disruption, particle size reduction, welding and vaporization, has been shown to be 99.99 percent effective in killing bacterial spores after only 30 seconds of non contact exposure in experiments conducted by researchers at Penn State and Ultran Labs, Boalsburg, Pa.
In the experiments, bacterial spores contained in a paper envelope, were placed slightly (3mm) above the active area of a specially equipped source of inaudible, high frequency (70

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…