
A NASA study finds that perennial sea ice in the Arctic is melting faster than previously thought–at a rate of 9 percent per decade. If these melting rates continue for a few more decades, the perennial sea ice will likely disappear entirely within this century, due to rising temperatures and interactions between ice, ocean and the atmosphere that accelerate the melting process.
Perennial sea ice floats in the polar oceans and remains at the end of the summer, when the ice cover is at its

Whether pregnant women with conditions ranging from ulcers to AIDS should keep taking the same doses of medicine they took before pregnancy is a question Medical College of Georgia researchers want answered.
They are betting they’ll find that to maintain efficacy, pregnant women will need higher doses and that the placenta, a 2-pound temporary organ of pregnancy, is why.
“The idea that we are developing is that pregnant women are so different from non-pregnant women in ter

What kind of mysteries and scientific intrigue await the European Space Agency’s Venus Express once it has left Earth for its nearest planetary neighbour in 2005? A closer inspection promises to reveal a planet that is hugely different from our own despite a few similarities.
Astronomers often call Venus the Earth’s twin because both are about the same size and have the same mass. In other ways, however, Venus seems to be an altogether different class of planet. Scientists are keen

Molekularabdrucke in Polymermaterialien als Reaktionsgefäße für die Pharmaforschung
Materialien mit winzigsten Hohlräumen, die andere Moleküle als “Gäste” aufnehmen können, spielen eine bedeutende Rolle in Wissenschaft und Technik. Ein besonders interessantes Verfahren zur Herstellung von Materialien mit passgenau zugeschnittenen Hohlräumen ist das so genannte “Molecular Imprinting”. Die als spätere Gäste vorgesehenen Moleküle werden dabei als Schablone eingesetzt: In ihrer Gegenwart

Ein Verfahren zur schnelleren Analyse von Wasserverschmutzung hat die australische Griffith University in Zusammenarbeit mit der Lincoln University in Neuseeland entwickelt. Organische Verschmutzungen können jetzt innerhalb einer Stunde nachgewiesen werden.
Bei der alten und bei der neuen Methode wird die organische Verschmutzung anhand des biochemischen Sauerstoffbedarfs in einer Wasserprobe gemessen. “Das bisherige Messverfahren dauert aber fünf Tage”, sagt Dr. Richard John vom Institut f
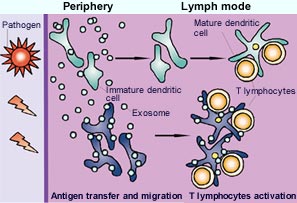
Exosomes are minute, natural membrane vesicles secreted by various types of cells of the immune system. They are of enormous interest to oncologists, who are now using them in clinical trials as tumor-antigen bearers to trigger tumor rejection by the body.
On the basis of studies in vitro and in mice, INSERM doctors and research scientists at the Institut Curie proposed a novel mode of functioning of exosomes in the December 2002 issue of Nature Immunology. It seems that exosomes can indire

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…