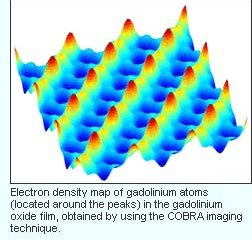
Scientists have developed and tested a new imaging technique that reveals the atomic structure of thin films with unprecedented resolution. For the first time, the technique has shown very precisely how the atoms of the first layers of a film rearrange under the action of the substrate on which the film is grown. The results of the study are reported as the cover story of the October issue of Nature Materials.
“This technique directly provides a very precise image of atomic positions within

An enzyme that plays a pivotal role in controlling genes in yeast acts through a more versatile mechanism than was previously thought to be the case, according to a new study by researchers at The Wistar Institute.
Its mode of action is also distinct from that of other members of the vital enzyme family into which it falls, the scientists found. Because the human counterpart of the enzyme has been associated with certain forms of leukemia, this observation raises the possibility that

A wheelchair robot developed by scientists at Coimbra University already has a prototype “capable of navigating without colliding with obstacles by commanded human voice”, as professor Urbano Nunes states, the person with joint responsibility, with professor Gabriel Pires, for the team of professors and students of the Electro-technical Engineering Department responsible for the project.
For the last five years this project has been developed and integrated in degree classes and pos

Scientists at UCLA’s Jonsson Cancer Center have developed the world’s first animal model for mature human B-cell lymphomas, a discovery that may lead to the uncovering of the genetic mutations that cause these types of cancer. Mature B-cell type lymphomas account for about 85 percent of all lymphomas.
The basic science discovery is outlined in the Oct. 29 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“What we can do now is grow cell

Genetically modified Bt crops are now widely used in the USA.
These crops contain genes from bacteria that make them toxic to some insect pests. A central concern in regulating these genetically modified crops is the risk of insects evolving resistance to the Bt toxins.
To reduce this risk, the “high dose/refuge” strategy is now being used, in which non-Bt fields (refuges for insect pests) are planted near Bt fields (where there is high dose of toxin).
In the Nove

Children who live with several siblings or who go to nurseries have less hay fever, but more asthma as adults, suggests a large international study in Thorax.
The findings are based on interviews with over 18,500 adults aged 20 to 44 from 36 countries in Europe, the USA, Australia and New Zealand. Blood samples were also taken from over 13,000 to measure levels of IgE, antibodies involved in the response to allergens such as house dust mite, cat, and grass.
Family size, access to

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How the body’s natural killer cells could fight leukemia. Every year, some 13,000 people in Germany are diagnosed with leukemia. Despite intensive chemotherapy, around one in two of them die….

… eco-friendly reactor converts air and water into ammonia. Producing enough ammonia to feed the world comes with a large carbon footprint;. process described in new UB-led study could help…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…