
Two scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) led a collaborative effort involving 18 researchers at half a dozen laboratories in the United States and Great Britain to determine the “proteome” of the most deadly form of the malaria pathogen – Plasmodium falciparum .
This study, in the current issue of the journal Nature, accompanies an article detailing the completion of a major six-year $17.9-million genome-sequencing effort involving 185 researchers from the United Kingd

Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI), Harvard University and the Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation have found a way to use a relatively new but readily available technology to quickly detect markers in the DNA of the most deadly type of malaria pathogen.
The technology could enable scientists and public health workers to identify the particular strain of malaria during an outbreak and determine if it is drug resistant or not.
“One of the reason
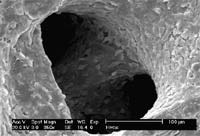
Researchers use flowing fluids to create mechanical stress needed for bone formation
A new study by Rice University researchers indicates that bioengineers growing bone in the laboratory may be able to create the mechanical stimulation needed to grow bone outside the body.
One of the greatest challenges tissue engineers face in growing bone in the laboratory is recreating the conditions that occur inside the body. The recipe for growing healthy bones includes not only a prec

For Karen Pressley, Duke’s new Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Center revealed critical details of her heart that could enable her to have an angioplasty.
Physicians at her home medical center in Fort Walton Beach, Fla. were reluctant to perform a heart procedure on 55-year-old Pressley because conventional techniques could not determine the extent of possible heart muscle death from a recent silent heart attack. So Pressley was referred to Duke University Medical Center, where cardiologi

By examining volcanic rocks retrieved from deep in the ocean, scientists have found they can estimate the carbon dioxide stored beneath much of the earth’s surface – a development that could enhance understanding of how volcanoes affect climate. The research by University of Florida scientists and others will be reported this week in the journal Nature.
Scientists examined chunks of basalt, a type of volcanic rock formed when lava cools, from 12,000 feet below the Pacific along a massiv

As anyone with a smattering of geological knowledge knows, Earth’s crust is made up of plates that creep over the planet’s surface at a rate of several inches per year. But why do they move the way they do? Even experts have had trouble teasing out the exact mechanisms.
A model developed by University of Michigan researchers and published in the Oct. 4 issue of Science provides a relatively simple explanation.
“It’s been known that slabs (portions of plates that ext

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…