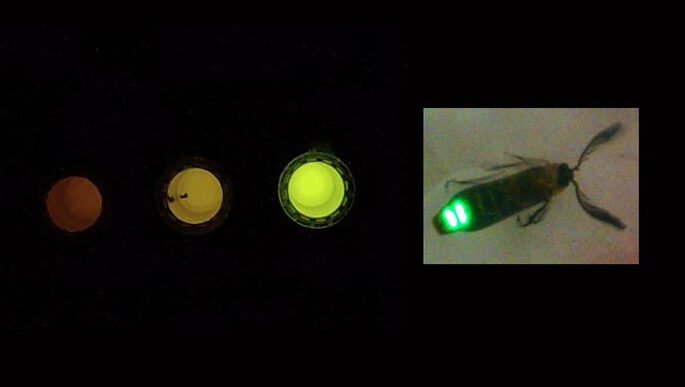
An enzyme cloned from an insect found by Brazilian researchers – and genetically modified – makes it possible to monitor intracellular acidity and could be used to study diseases and drugs. The gene encoding an enzyme from a firefly, discovered at the Sorocaba campus of the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in Brazil, has given rise to a biosensor capable of detecting pH changes in mammalian cells – which could be useful, for example, in studying diseases and assessing…
More than two-fifths of Oregon community pharmacies require a prescription to purchase syringes, even though they can be sold over the counter, creating an access barrier that could exacerbate the spread of bloodborne diseases like hepatitis C. Oregon State University researchers conducted a telephone survey of more than 400 pharmacies in Oregon and learned that 43% of them were unwilling to sell a 10-pack of syringes to someone without a prescription. The scientists say the study was the largest to…
This Sea Grant publication will serve as a valuable resource for fish farmers and policymakers navigating the complex legal environment of aquaculture Fish farmers across the Great Lakes states can face a confusing web of permits, policies and regulations that can hinder the growth of their operations. A new Sea Grant publication, Aquaculture Regulations in the Great Lakes, offers much-needed clarity. The report breaks down complex legal frameworks and provides practical insights to help aquaculture producers understand and navigate state and…
Annual award given to a researcher perceived as a major creative force, actively generating new concepts in nutrition The American Society for Nutrition, or ASN, and the ASN Foundation announced the distinguished recipients of the 2025 National Scientific Achievement Awards today. Recognizing outstanding contributions and pioneering advancements in the field of nutrition, these awards serve as a testament to excellence and innovation. Among the honorees is Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Dr. Leanne Redman, who received the E. V. McCollum Award…

Study reveals new information about how to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can cause cells to abandon this characteristic and enter a zombie-like state known as senescence where they persist but no longer divide to make new cells. Our bodies can remove…

University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds’ song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages. The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird’s brain involved with singing, dramatically…

A new type of antibody which stimulates the immune system to target cancer cells slows tumor growth, according to new research Antibody treatment which activates the patient’s own immune system against cancer, known as immunotherapy, is increasingly being investigated as an alternative for chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This is because it specifically targets the cancer cells, which reduces the side effects seen with more conventional therapies. Tumours, such as some breast and ovarian cancers, can express the marker HER2. HER2 is…

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

Study links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology. Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their…

Understanding children’s subjective experiences through color As a child, did it ever occur to you that your perception of color differed from that of others? It’s quite common to have this thought, but it turns out that the human color experience may be more universal than we previously believed. In psychology and neuroscience, the relationship between subjective experience, such as how we perceive color, and physical brain activity has remained an unresolved problem. Furthermore, due to their limited language abilities,…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. Observed by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, the galaxy – designated JADES-GS-z14-0 – is unexpectedly bright and chemically complex for an object from this primordial era, the researchers said. This provides a rare glimpse into the universe’s earliest chapter. The findings, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, build…

Physics professor J. Ping Liu helps boost nation’s energy security and advance toward a world-class magnet research hub University of Texas at Arlington physics Professor J. Ping Liu has won the 2025 Hill Prize in Physical Sciences for pioneering new ways to design magnets that power high-tech devices. Awarded by the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST) and Lyda Hill Philanthropies, the prize recognizes groundbreaking innovations with the potential for real-world impact. Dr. Liu shares the award as co-principal…
A metamaterial with potential applications in sensor technology A flower-shaped structure only a few micrometres in size made of a nickel-iron alloy can concentrate and locally enhance magnetic fields. The size of the effect can be controlled by varying the geometry and number of ‘petals’. This magnetic metamaterial developed by Dr Anna Palau’s group at the Institut de Ciencia de Materials de Barcelona (ICMAB) in collaboration with her partners of the CHIST-ERA MetaMagIC project, has now been studied at BESSY…

New machine learning model cuts fluid simulation time from 45 minutes to 3 AI has created a sea change in society; now, it is setting its sights on the sea itself. Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a machine learning-powered fluid simulation model that significantly reduces computation time without compromising accuracy. Their fast and precise technique opens up potential applications in offshore power generation, ship design and real-time ocean monitoring. Accurately predicting fluid behavior is crucial for industries relying…

A machine-learning algorithm to study the behavior of proteins within cells and to predict their ability to trigger neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s. The study published in Genome Biology A research group led by Gian Gaetano Tartaglia, Principal Investigator at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT), developed a machine-learning algorithm to study the behavior of proteins within cells and to predict their ability to trigger neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s,…

An AI model trained on large amounts of genetic data can predict whether bacteria will become antibiotic-resistant. The new study shows that antibiotic resistance is more easily transmitted between genetically similar bacteria and mainly occurs in wastewater treatment plants and inside the human body. “By understanding how resistance in bacteria arises, we can better combat its spread. This is crucial to protect public health and the healthcare system’s ability to treat infections,” says Erik Kristiansson, Professor at the Department of…

Norah Saarman receives American Mosquito Control Association Research Fund grant to develop improved species identification method Morphology is the study of the form and structure of organisms, including their physical characteristics such as shape, size and arrangement of parts. Morphology is key to taxonomy, the science of classifying organisms, as scientists use morphology to identify and study species, as well as to explore evolutionary processes. Identifying species is challenging — even with large animals and plants, says Utah State University…
As discussed in the paper, the fear of public speaking is widely cited as being the most common fear. Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that the prevalence of social anxiety and a fear of public speaking are both on the rise. This is concerning when one considers the range of known subsequent negative impacts on mental health, physical health, academic attainment, and career progression. To address this, Dr Chris Macdonald created an online platform where users transform into skilled…

Groundbreaking research by physicists at The City College of New York is being credited for a novel discovery regarding the interaction of electronic excitations via spin waves. The finding by the Laboratory for Nano and Micro Photonics (LaNMP) team headed by physicist Vinod Menon could open the door to future technologies and advanced applications such as optical modulators, all-optical logic gates, and quantum transducers. The work is reported in the journal Nature Materials. The researchers showed the emergence of interaction…

Warwick astronomers discover the first double white dwarf binary, destined to explode as type 1a supernova University of Warwick astronomers have discovered an extremely rare, high mass, compact binary star system only ~150 light years away. These two stars are on a collision course to explode as a type 1a supernova, appearing 10 times brighter than the moon in the night sky. Type 1a supernovae are a special class of cosmic explosion, famously used as ‘standard candles’ to measure distances…

The research team now believes that Aguas Zarcas is strong because it avoided collisions in space and did not have the cracks that weaken many meteorites. In the Pinball World of Asteroids, a Mudball Meteorite Avoided Collisions March 31, 2025, Mountain View, CA — In April 2019, rare primitive meteorites fell near the town of Aguas Zarcas in northern Costa Rica. In an article published online in the journal Meteoritics & Planetary Science, an international team of researchers describe the…

As part of its commitment to unraveling the universe’s mysteries through sustained support of the astrophysics community, the Flatiron Institute is securing the future of MESA (Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics), an open-source software suite that has transformed how researchers model the evolution of stars. As MESA’s creator, Bill Paxton, steps down, the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics (CCA) is stepping up to support MESA’s need for ongoing maintenance and continued development. CCA has hired Philip Mocz as…

From seat cushions to mattresses to insulation, foam is everywhere — even if we don’t always see it. Now, researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas have fused chemistry with technology to create a 3D-printed foam that is more durable and more recyclable than the polymer foam found in many everyday products. The research, which appears in the March 1 print edition of RSC Applied Polymers, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry, focused on creating a sturdy but lightweight foam…
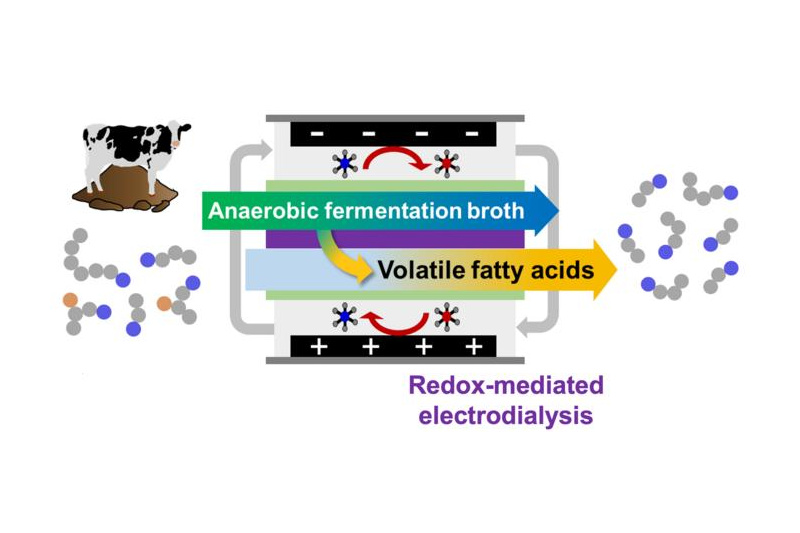
A collaboration between chemical engineers and animal scientists has created a system for recovering valuable industrial chemicals from animal waste, representing a major step towards circularity and environmental sustainability. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a nanofiltration system for separating volatile fatty acids (VFAs) – organic molecules that are critical in fine chemical production across many sectors – from cattle manure fermented in bioreactors. Thanks to the incorporation of selective ion-exchange membranes into an electrochemical separation system,…

Findings show that radiation-induced chemistry may mitigate metal alloy corrosion in nuclear reactors cooled by molten salts High temperatures and ionizing radiation create extremely corrosive environments inside a nuclear reactor. To design long-lasting reactors, scientists must understand how radiation-induced chemical reactions impact structural materials. Chemists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Idaho National Laboratory recently performed experiments showing that radiation-induced reactions may help mitigate the corrosion of reactor metals in a new type of reactor…

Research hints at calcium’s potential role in enforcing a specific molecular handedness among primitive polyesters and early biomolecules A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Institute of Science Tokyo has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality). Like our left…

Bilayer device can control many forms of polarized light Almost a decade ago, Harvard engineers unveiled the world’s first visible-spectrum metasurfaces – ultra-thin, flat devices patterned with nanoscale structures that could precisely control the behavior of light. A powerful alternative to traditional, bulky optical components, metasurfaces today enable compact, lightweight, multifunctional applications ranging from imaging systems and augmented reality to spectroscopy and communications. Now, researchers in the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) are doubling down, literally, on metasurface…

Researchers have discovered an unexpected superconducting transition in extremely thin films of niobium diselenide (NbSe₂). Published in Nature Communications, they found that when these films become thinner than six atomic layers, superconductivity no longer spreads evenly throughout the material, but instead becomes confined to its surface. This discovery challenges previous assumptions and could have important implications for understanding superconductivity and developing advanced quantum technologies. Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have made a surprising discovery about how superconductivity behaves…

A metamaterial with potential applications in sensor technology A flower-shaped structure only a few micrometres in size made of a nickel-iron alloy can concentrate and locally enhance magnetic fields. The size of the effect can be controlled by varying the geometry and number of ‘petals’. This magnetic metamaterial developed by Dr Anna Palau’s group at the Institut de Ciencia de Materials de Barcelona (ICMAB) in collaboration with her partners of the CHIST-ERA MetaMagIC project, has now been studied at BESSY…

Using machine learning workflows developed in-house, the researchers were able to establish that heat conduction is much more intricate than previously thought. Findings offer potential for developing specific materials. Complex materials such as organic semiconductors or the microporous metal-organic frameworks known as MOFs are already being used for numerous applications such as OLED displays, solar cells, gas storage and water extraction. Nevertheless, they still harbour a few secrets. One of these has so far been a detailed understanding of how…

Study shows contrast between wet and dry areas increases rain by up to 30% Storm forecasting is traditionally based on studying atmospheric conditions but ground-breaking research that also looks at land surface conditions is set to transform early warning systems in tropical regions. This will enable communities to better adapt to the destructive impacts of climate change. The new study led by the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH) has shown that a large contrast in soil moisture levels…

Plate temperature and water release can explain the occurrence of different types of earthquakes in Guerrera, Mexico. The Kobe University simulation study also showed that the shape of the Cocos Plate is responsible for a gap where earthquakes haven’t occurred for more than a century. The results are important for accurate earthquake prediction models in the region. Where one tectonic plate is pushed down by another, the resulting stress is released in various tectonic events. There are catastrophic megathrust earthquakes,…

Deep below Earth’s surface, rock and mineral formations lay hidden with a secret brilliance. Under a black light, the chemicals fossilized within shine in brilliant hues of pink, blue and green. Scientists are using these fluorescent features to understand how the caves formed and how life is supported in extreme environments, which may reveal how life could persist in faraway places, like Jupiter’s icy moon Europa. The researchers will present their results at the spring meeting of the American Chemical…

Recent studies have shown that carbon stocks in terrestrial ecosystems are increasing, mitigating around 30% of the CO2 emissions linked to human activities. The overall value of carbon sinks on the earth’s surface is fairly well known—as it can be deduced from the planet’s total carbon balance anthropogenic emissions, the accumulation of carbon in the atmosphere and the ocean sinks—yet, researchers know very little about carbon distribution between the various terrestrial pools: living vegetation—mainly forests—and nonliving carbon pools—soil organic matter,…