
For years scientists have been studying the impact of different geophysical fields on the earthquakes occurrence. It has been assumed that the fields, generated due to the solar activity, earth flows fluctuations, the Earth`s speed of rotation and even the launch of magnetohydrodynamic generators affect the strained state of the earth`s crust, these fields `pumping` additional energy into the crust. Normally the aroused earthquakes are recorded several days after the provoking key event.

Because living organisms contain millions of different molecules, identifying or separating any single one of these from their natural environment in order to carry out research work or perform diagnoses is quite like looking for a needle in a haystack. A number of molecular separation technologies are of course available, and are used by laboratories on a daily basis, but they are often unwieldy and costly. Scientists the world over are therefore attempting to develop a new generation of analytic de

Martian atmosphere churns harder in south making north wetter.
Scientists have figured out why it’s wet up north – on Mars. A new computer simulation of the martian atmosphere suggests that the planet’s geography causes differences in atmospheric circulation within the northern and southern hemispheres. These differences dump more water on the martian north pole, where it adds to the seasonal ice-cap.
Mark Richardson of the California Institute of Technology in Pasa

Knee-high relative of Triceratops unearthed.
The fearsome horns and bony neck plates of Triceratops have scared generations of kids. Now fossil finds reveal that its predecessor was a little more huggable: it was a dog-sized creature with a beak.
Triceratops is the most famous member of the late ceratopsians, which were rhinoceros-like dinosaurs with horns. Little is known about the early evolution of this large and varied group of plant-eaters because their fo
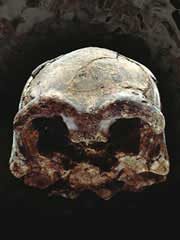
Ethiopian fossil suggests early humans were one big family.
A one-million-year-old skull unearthed in Ethiopia hints that our long-extinct cousins Homo erectus were a varied and widespread bunch, much like today’s humans. The find may undermine previous claims that H. erectus was in fact made up of two different species. Homo erectus , which means ’upright man’, appeared about 1.8 million years ago. Because of its posture and large brain, it is regarded as t

A University of Plymouth lecturer and his PhD student are putting Plymouth on the world map for research in a specialist field of marine biology: the importance of seagrass meadows.
Seagrass can grow prolifically in outer estuarine areas and is the only flowering plant fully adapted for life in the marine environment. As well as being home to a wide variety of animal life including fish such as sea horses, its dense beds offer some protection against wave buffeting and the ensuing coastal e

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…