
Report assesses chemical effects of Gulf war weapon.
Depleted uranium in weapons may have left some soldiers with kidney damage and could cause long-term environmental contamination, say British scientists. Their independent review calls for accurate exposure tests and long-term environmental monitoring in combat zones.
Depleted uranium (DU) is a dense radioactive substance. It was used in weapons to punch through heavily armoured vehicles during the Gulf War and Kosovo conf

A lack of investment in corporate research may be counterproductive to industry says Dr Elsa Reichmanis, director of Materials Research at Lucent Technologies` Bell Labs, New Jersey, USA. In an exclusive Tomorrow’s Leaders online broadcast, Reichmanis stated ‘In order to succeed in the long term, investment in the future is a must, and that means investment in research.’
Dr Reichmanis made her remarks during a one-hour live broadcast at www.tomorrows-leaders.net. She answered questions fr

There are two ways of dealing with the problem of nuclear waste. The first one is the easiest but not the most sensible: you can simply bury nuclear waste products and try to forget about them. However, this way does not seem to be the most rational. It seems much more attractive to try to derive some benefit from the situation. In this case it is worth extracting the compounds that could be used in future from the whole mass of nuclear wastes. In the first instance, these are non-burnt uranium and p

There are no in-car methods of detecting that a driver is too drunk to drive – until now. A team at Bristol University, led by physiologist Dr Dilwyn Marple-Horvat, has found a new way of detecting whether a driver has drunk too much to be fit to be at the wheel.
To assess a driver`s fitness to drive, a new device has been created that measures the degree of co-ordination between hand and eye. It uses: an in-car eye-tracker; a system that continuously monitors steering wheel movements; and

Technology unravels mysteries of ancient corpse.
Glassy-eyed with a hole in the head – meet Nesperennub, the virtual-reality mummy. A new three-dimensional reconstruction of his insides swoops through musty layers of linen to penetrate his holy skull, without putting the ancient artefact at risk.
Egyptologist John Taylor smuggled the British Museum’s sealed coffin into a hospital computerized tomography (CT or CAT) scanner after hours. The resulting 1,500 flat scans hav
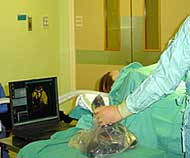
Virtual organ image beamed into OR.
Liver surgeon Rory McCloy carries a wad of CAT scans into his operations. “I spend my life looking at 60 slices of salami,” he says. Peering at the light-box, he constructs a mental picture of a tumour before making a cut. “I’m trying to do a 3D operation with 2D images,” he protests.
Despite the wide availability of 3D graphics programs, they rarely penetrate operating theatres. Frustrated by the technology void, McCloy, of Manchester Roy

– new calculation confirms standard model of particle physics. Contribution of hadronic vacuum polarization determined with unprecedented accuracy. The magnetic moment of the muon is an important precision parameter for…
Technique may prevent formation of unwanted waves that siphon off needed energy. Heating plasma to the ultra-high temperatures needed for fusion reactions requires more than turning the dial on a…

An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

Antibody that Neutralizes Inhibitory Factors Involved in Nerve Regeneration Leads to Enhanced Motor Function after Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Researchers at 13 clinics in Germany, Switzerland, the Czech Republic and…

How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable…

“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

The quest for sustainable energy solutions has been a major focus of scientific research for decades. Solar energy, a clean and renewable source, has emerged as a promising alternative to…

With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…