
Combining Hubble Space Telescope images with radio observations has revealed a highly unusual system consisting of a fast spinning pulsar and a bloated red companion star. The existence of the system is something of a mystery – the best explanation so far is that we have our first view of a millisecond pulsar just after it has been `spun up` by its red companion star.
Although more than 90 specimens of the exotic species of fast-spinning `millisecond pulsars` are known today, no observation
For decades, atomic clocks have been the pinnacle of precision timekeeping, enabling GPS navigation, cutting-edge physics research, and tests of fundamental theories. But researchers at JILA, led by JILA and NIST Fellow and University of Colorado Boulder physics professor Jun Ye, in collaboration with the Technical University of Vienna, are pushing beyond atomic transitions to something potentially even more stable: a nuclear clock. This clock could revolutionize timekeeping by using a uniquely low-energy transition within the nucleus of a thorium-229…
By David Chandler WOODS HOLE, Mass. – The impact of hurricanes when they travel over land, or when they affect ships or oil-drilling platforms, are quite well understood. But these huge cyclones also stir up the ocean itself, with consequences that are relatively unknown and hard to study. But a unique, subsurface experimental platform moored to the floor of the Sargasso Sea, about 47 miles southeast of Bermuda, is changing that. With collection points at increasing depths along the mooring…
Researchers at Heriot-Watt University have made a ground-breaking discovery paving the way for a transformative era in photonic technology. For decades, scientists have theorised the possibility of manipulating the optical properties of light by adding a new dimension—time. This once-elusive concept has now become a reality thanks to nanophotonics experts from the School of Engineering and Physical Sciences in Edinburgh, Scotland. The team’s breakthrough emerged from experiments with nanomaterials known as transparent conducting oxides (TCOs) – a special glass capable…

Study reveals new information about how to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can cause cells to abandon this characteristic and enter a zombie-like state known as senescence where they persist but no longer divide to make new cells. Our bodies can remove…

University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds’ song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages. The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird’s brain involved with singing, dramatically…

A new type of antibody which stimulates the immune system to target cancer cells slows tumor growth, according to new research Antibody treatment which activates the patient’s own immune system against cancer, known as immunotherapy, is increasingly being investigated as an alternative for chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This is because it specifically targets the cancer cells, which reduces the side effects seen with more conventional therapies. Tumours, such as some breast and ovarian cancers, can express the marker HER2. HER2 is…

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

Study links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology. Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their…

Understanding children’s subjective experiences through color As a child, did it ever occur to you that your perception of color differed from that of others? It’s quite common to have this thought, but it turns out that the human color experience may be more universal than we previously believed. In psychology and neuroscience, the relationship between subjective experience, such as how we perceive color, and physical brain activity has remained an unresolved problem. Furthermore, due to their limited language abilities,…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. Observed by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, the galaxy – designated JADES-GS-z14-0 – is unexpectedly bright and chemically complex for an object from this primordial era, the researchers said. This provides a rare glimpse into the universe’s earliest chapter. The findings, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, build…

Physics professor J. Ping Liu helps boost nation’s energy security and advance toward a world-class magnet research hub University of Texas at Arlington physics Professor J. Ping Liu has won the 2025 Hill Prize in Physical Sciences for pioneering new ways to design magnets that power high-tech devices. Awarded by the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST) and Lyda Hill Philanthropies, the prize recognizes groundbreaking innovations with the potential for real-world impact. Dr. Liu shares the award as co-principal…
Researchers have advanced a decades-old challenge in the field of organic semiconductors, opening new possibilities for the future of electronics. The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge and the Eindhoven University of Technology, have created an organic semiconductor that forces electrons to move in a spiral pattern, which could improve the efficiency of OLED displays in television and smartphone screens, or power next-generation computing technologies such as spintronics and quantum computing. The semiconductor they developed emits circularly polarised light—meaning…

We all know someone who seems to defy aging—people who look younger than their peers despite being the same age. What’s their secret? Scientists at Osaka University (Japan) may have found a way to quantify this difference. By incorporating hormone (steroid) metabolism pathways into an AI-driven model, they have developed a new system to estimate a person’s biological age a measure of how well their body has aged, rather than just counting the years since birth. Using just five drops…

As the planet warms, Antarctica’s ice sheet is melting and contributing to sea-level rise around the globe. Antarctica holds enough frozen water to raise global sea levels by 190 feet, so precisely predicting how it will move and melt now and in the future is vital for protecting coastal areas. But most climate models struggle to accurately simulate the movement of Antarctic ice due to sparse data and the complexity of interactions between the ocean, atmosphere, and frozen surface. In…

CAM is proposed to highlight the class-related activation regions for an image classification network, where feature positions related to the specific object class are activated and have higher scores while other regions are suppressed and have lower scores. For specific visual tasks, CAM can be used to infer the object bounding boxes in weakly-supervised object location(WSOL) and generate pseudo-masks of training images in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS). Therefore, obtaining the high-quality CAM is very important to improve the recognition performance…
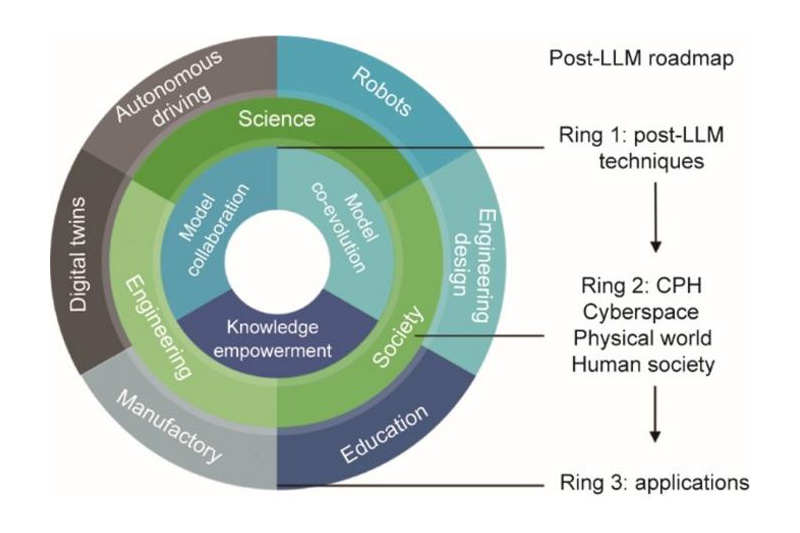
A recent paper published in the journal Engineering delves into the future of artificial intelligence (AI) beyond large language models (LLMs). LLMs have made remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they face limitations such as outdated information, hallucinations, inefficiency, and a lack of interpretability. To address these issues, researchers explore three key directions: knowledge empowerment, model collaboration, and model co-evolution. Knowledge empowerment aims to integrate external knowledge into LLMs. This can be achieved through various methods, including integrating knowledge into training objectives,…
As discussed in the paper, the fear of public speaking is widely cited as being the most common fear. Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that the prevalence of social anxiety and a fear of public speaking are both on the rise. This is concerning when one considers the range of known subsequent negative impacts on mental health, physical health, academic attainment, and career progression. To address this, Dr Chris Macdonald created an online platform where users transform into skilled…

For decades, atomic clocks have been the pinnacle of precision timekeeping, enabling GPS navigation, cutting-edge physics research, and tests of fundamental theories. But researchers at JILA, led by JILA and NIST Fellow and University of Colorado Boulder physics professor Jun Ye, in collaboration with the Technical University of Vienna, are pushing beyond atomic transitions to something potentially even more stable: a nuclear clock. This clock could revolutionize timekeeping by using a uniquely low-energy transition within the nucleus of a thorium-229…

Researchers at Heriot-Watt University have made a ground-breaking discovery paving the way for a transformative era in photonic technology. For decades, scientists have theorised the possibility of manipulating the optical properties of light by adding a new dimension—time. This once-elusive concept has now become a reality thanks to nanophotonics experts from the School of Engineering and Physical Sciences in Edinburgh, Scotland. The team’s breakthrough emerged from experiments with nanomaterials known as transparent conducting oxides (TCOs) – a special glass capable…

A team of researchers from the University of Ottawa has made significant strides in understanding the ionization of atoms and molecules, a fundamental process in physics that has implications for various fields including x-ray generation and plasma physics. Think about atoms – the building blocks of everything around us. Sometimes, they lose their electrons and become charged particles (that’s ionization). It happens in lightning, in plasma TVs, and even in the northern lights. Until now, scientists thought they could only…

Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder to characterize Moon’s mantle Just hours after touching down on the surface of the Moon on March 2 aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost 1 lander, the Southwest Research Institute-led Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS) was activated and deployed its five sensors to study the Moon’s interior by measuring electric and magnetic fields. The LMS instrument is the first extraterrestrial application of magnetotellurics. “For more than 50 years, scientists have used magnetotellurics on Earth for a wide variety of…

Mesopore introduction enables world-class hydrogen peroxide production characteristics even in low oxygen air supply environments Hydrogen peroxide is one of the world’s top 100 industrial chemicals with a wide range of applications in the chemical, medical, and semiconductor industries. Currently, hydrogen peroxide is mainly produced through the anthraquinone process, but this process has several problems, including high energy consumption, the use of expensive palladium catalysts, and environmental pollution due to by-products. In recent years, an environmentally friendly method of producing…

Hundreds of regular patterns spontaneously form on a small germanium chip Key takeaways UCLA doctoral student Yilin Wong noticed that some tiny dots had appeared on one of her samples, which had been accidentally left out overnight. The layered sample consisted of a germanium wafer topped with evaporated metal films in contact with a drop of water. On a whim, she looked at the dots under a microscope and couldn’t believe her eyes. Beautiful spiral patterns had been etched into the…

By Leah Shaffer Much of cell behavior is governed by the actions of biomolecular condensates: building block molecules that glom together and scatter apart as needed. Biomolecular condensates constantly shift their phase, sometimes becoming solid, sometimes like little droplets of oil in vinegar, and other phases in between. Understanding the electrochemical properties of such slippery molecules has been a recent focus for researchers at Washington University in St. Louis. In research published in Nature Chemistry, Yifan Dai, assistant professor of…

Butterflies are disappearing in the United States. All kinds of them. With a speed scientists call alarming, and they are sounding an alarm. A sweeping new study published in Science for the first time tallies butterfly data from more than 76,000 surveys across the continental United States. The results: between 2000 and 2020, total butterfly abundance fell by 22% across the 554 species counted. That means that for every five individual butterflies within the contiguous U.S. in the year 2000,…

Researchers have advanced a decades-old challenge in the field of organic semiconductors, opening new possibilities for the future of electronics. The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge and the Eindhoven University of Technology, have created an organic semiconductor that forces electrons to move in a spiral pattern, which could improve the efficiency of OLED displays in television and smartphone screens, or power next-generation computing technologies such as spintronics and quantum computing. The semiconductor they developed emits circularly polarised light—meaning…

UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering research created inorganic and polymer battery electrolytes simultaneously, with potential applications across chemistry Creating battery electrolytes – the component that carries the charged particles back and forth between a battery’s two terminals – has always been a tradeoff. Solid-state inorganic electrolytes move the particles extremely efficiently, but being solid and inorganic means they’re also brittle, hard to work with and difficult to connect seamlessly with the terminals. Polymer electrolytes are a dream to work…

Using first-principles calculations, a research group led by Prof. WANG Xianlong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, found that phosphorus doping is an effective way to achieve high-energy polymeric nitrogen with black-phosphorus structure (BP-N) stable at ambient pressure. The research results were published in Matter and Radiation at Extremes. Cubic gauche nitrogen with diamond-like structure and BP-N with black phosphorus structure, represented by polymeric all-nitrogen materials, are a class of high-energy density materials composed…

Quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) have made rapid progress in luminescence, efficiency, and stability, making them promising candidates for displays and solid-state lighting applications. However, achieving high-performance QLEDs with high color purity remains a persistent challenge, particularly red QLEDs, thus limiting the popularity of ultra-high definition devices. Recently, Soochow University, in collaboration with Macau University of Science and Technology and other research institutes, reported a facile high-temperature successive ion layer adsorption and reaction (HT-SILAR) strategy for the growth of high-quality,…

By David Chandler WOODS HOLE, Mass. – The impact of hurricanes when they travel over land, or when they affect ships or oil-drilling platforms, are quite well understood. But these huge cyclones also stir up the ocean itself, with consequences that are relatively unknown and hard to study. But a unique, subsurface experimental platform moored to the floor of the Sargasso Sea, about 47 miles southeast of Bermuda, is changing that. With collection points at increasing depths along the mooring…

The study shows that the regional water availability constrains the current and future production of 32 geological resources Geological resources such as critical metals and minerals, essential for the diffusion of technologies such as renewable energy and energy storage towards a decarbonized society, are indispensable for supporting modern life in the form of various products and services. Their demand is expected to increase in the coming years owing to global population as well as economic growth. Thus far, scientists and…

Faster identification of fish sounds from acoustic recordings can improve research, conservation efforts Coral reefs are some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems. Despite making up less than 1% of the world’s oceans, one quarter of all marine species spend some portion of their life on a reef. With so much life in one spot, researchers can struggle to gain a clear understanding of which species are present and in what numbers. In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical…

Some parts of Hawai‘i are sinking faster than others. That discovery, published recently in a study by researchers at the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa, also highlights that as sea level rises, the infrastructure, businesses, and communities in these low-lying areas are at risk of flooding sooner than scientists anticipated, particularly in certain urban areas of O‘ahu. “Our findings highlight that subsidence is a major, yet often overlooked, factor in assessments of future flood exposure,” said Kyle Murray, lead…