
Adolescents from families where mealtimes and other activities are shared seem to have fewer mental health problems, reports a study in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
Researchers assessed the family habits and rituals of 82 first time users, aged between 14 and 23, of mental health services in one metropolitan area. Anxiety and depression were the main problems for which treatment was sought. Family practices in 177 young people within the same age band from various educa
Spinal cord injuries are life-altering, often leaving individuals with severe mobility impairments. While rehabilitation robotics—devices that guide movement during therapy—have improved training for those with spinal cord injuries, their effectiveness remains limited. Without active muscle engagement, robotic-assisted movement alone does not sufficiently retrain the nervous system. A team at .NeuroRestore, led by Grégoire Courtine and Jocelyne Bloch, has now developed a system that seemlessly integrates an implanted spinal cord neuroprosthesis with rehabilitation robotics. The researchers’ device delivers well-timed electrical pulses…
University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds’ song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages. The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird’s brain involved with singing, dramatically…
By Leah Shaffer Much of cell behavior is governed by the actions of biomolecular condensates: building block molecules that glom together and scatter apart as needed. Biomolecular condensates constantly shift their phase, sometimes becoming solid, sometimes like little droplets of oil in vinegar, and other phases in between. Understanding the electrochemical properties of such slippery molecules has been a recent focus for researchers at Washington University in St. Louis. In research published in Nature Chemistry, Yifan Dai, assistant professor of…

A JCAP study proposes a test for the Cosmological Principle using weak gravitational lensing “The cosmological principle is like an ultimate kind of statement of humility,” explains James Adam, astrophysicist at the University of the Western Cape, Cape Town, South Africa, and lead author of the new paper. According to the Cosmological Principle, not only are we not at the center of the Universe, but a true center does not exist. A further assumption, similar to but distinct and independent…

ISTA scientists uncover how the brain unblurs vision during movement Why do our mental images stay sharp even when we are moving fast? A team of neuroscientists led by Professor Maximilian Jösch at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) has identified a mechanism that corrects visual distortions caused by movement in animals. The study, conducted in mice, identifies a core function that can be generalized across the vertebrate visual system, including primates such as humans. The findings are…

A UCLA research team has found that drugs being sold as fentanyl contain high amounts of the industrial chemical bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) sebacate, or BTMPS. This new substance of concern emerged in the illicit drug supply nearly simultaneously in multiple U.S. locations from coast-to-coast. From June through October 2024, the team quantitatively tested samples of drugs sold as fentanyl that had high levels of the chemical, which belongs to a class of compounds called hindered amine light stabilizers and has a variety…

Measurements and data collected from space can be used to better understand life on Earth. An ambitious, multinational research project funded by NASA and co-led by UC Merced civil and environmental engineering Professor Erin Hestir demonstrated that Earth’s biodiversity can be monitored and measured from space, leading to a better understanding of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Hestir led the team alongside University of Buffalo geography Professor Adam Wilson and Professor Jasper Slingsby from the University of Cape Town on BioSCape, which collected data over six…

Discovery creates opportunities to study therapeutic properties of ibogaine and related compounds Ibogaine — a psychoactive plant derivative — has attracted attention for its anti-addictive and anti-depressant properties. But ibogaine is a finite resource, extracted from plants native to Africa like the iboga shrub (Tabernanthe iboga) and the small-fruited voacanga tree (Voacanga africana). Further, its use can lead to irregular heartbeats, introducing safety risks and an overall need to better understand how its molecular structure leads to its biological effects….

Improved approach to marine conservation aligns ecological restoration with human well-being Could 2025 be the year marine protection efforts get a “glow up”? According to a team of conservation-minded researchers, including Octavio Aburto of UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, the moment has arrived. In a new study published Feb. 6 in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, Aburto and a multinational team of marine scientists and economists unveil a comprehensive framework for Marine Prosperity Areas, or MPpAs. With…

UCalgary scientist says it’s important to determine what happened and what can be learned Experts from the global Earth science community – including a scientist from the University of Calgary – have pieced together what happened during the massive Sikkim flood to try to help others prepare for similar disasters. On Oct. 3, 2023, a multi-hazard cascade in the Sikkim Himalaya, India, was triggered by a permanently frozen (permafrost) lateral moraine – debris from erosion along a glacier – collapsing…

Grant enables study into mechanical properties of episiotomy cuts Millions of women undergo episiotomies during childbirth every year, yet the mechanics behind these surgical cuts remain largely unstudied. A new research project is poised to change that, addressing this significant gap in women’s health. An episiotomy involves cutting the pelvic-floor muscles to aid delivery, a technique currently guided largely by a surgeon’s personal judgment and experience. While intended to prevent severe vaginal tears or other complications during delivery, the procedure…
How simulations help manufacturing of modern displays. Modern materials must be recyclable and sustainable. Consumer electronics is no exception, with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) taking over modern televisions and portable device displays. However, the development of suitable materials – from the synthesis of molecules to the production of display components – is very time-consuming. Scientists led by Denis Andrienko of the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research and Falk May from Display Solutions at Merck have now developed a simulation…

CAM is proposed to highlight the class-related activation regions for an image classification network, where feature positions related to the specific object class are activated and have higher scores while other regions are suppressed and have lower scores. For specific visual tasks, CAM can be used to infer the object bounding boxes in weakly-supervised object location(WSOL) and generate pseudo-masks of training images in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS). Therefore, obtaining the high-quality CAM is very important to improve the recognition performance…
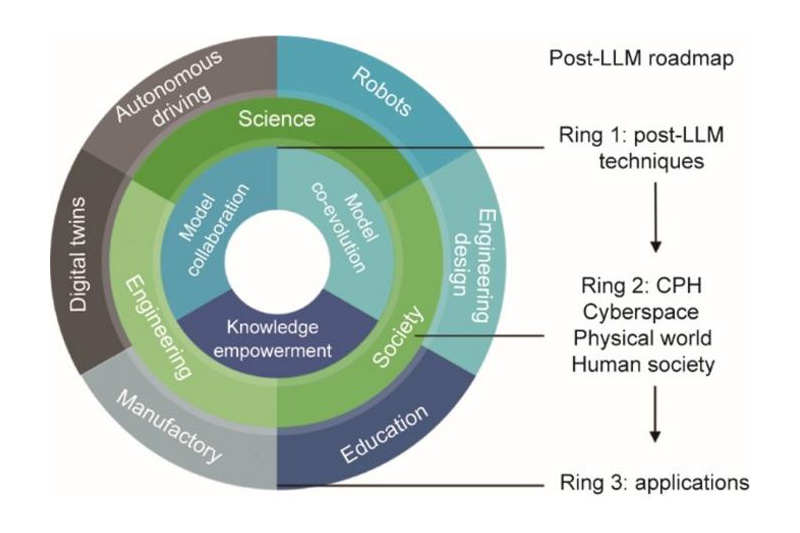
A recent paper published in the journal Engineering delves into the future of artificial intelligence (AI) beyond large language models (LLMs). LLMs have made remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they face limitations such as outdated information, hallucinations, inefficiency, and a lack of interpretability. To address these issues, researchers explore three key directions: knowledge empowerment, model collaboration, and model co-evolution. Knowledge empowerment aims to integrate external knowledge into LLMs. This can be achieved through various methods, including integrating knowledge into training objectives,…

Hyperspectral imaging and AI can identify individuals using blood vessels in palms Hyperspectral imaging is a technology that detects slight differences in color to pinpoint the characteristics and conditions of an object. While a normal camera creates images using red, green, and blue, a hyperspectral camera can obtain over 100 images in the visible to near-infrared light range in a single shot. As a result, hyperspectral imaging can obtain information that the human eye cannot see. Specially Appointed Associate Professor…

Q&A with Brendan Cottrell, who investigated the use of smartphones to create 3D scans of stranded marine life that can help scientists protect marine species What inspired you to become a researcher? My interest in research began with an early love for nature, particularly the ocean and its wildlife. Drawn to conservation, I am fascinated by how technology can help study and protect marine mammals. Can you tell us about the research you’re currently working on? This research focuses on…
A dynamic left-hand squeeze helps to optimize performance. The images are legendary: Tennis stars who hit the deciding match ball just outside the line, golfers who putt the ball past the cup from only inches away, and speakers who suddenly can’t say a word. These individuals all have one thing in common: They are unable to access their performance abilities in a crucial situation. A research team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) investigated the phenomenon and has come…

Advancing the search for weird life on weird planets Scientists have identified a promising new way to detect life on faraway planets, hinging on worlds that look nothing like Earth and gases rarely considered in the search for extraterrestrials. In a new Astrophysical Journal Letters paper, researchers from the University of California, Riverside, describe these gases, which could be detected in the atmospheres of exoplanets — planets outside our solar system — with the James Webb Space Telescope, or JWST….

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. Observed by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, the galaxy – designated JADES-GS-z14-0 – is unexpectedly bright and chemically complex for an object from this primordial era, the researchers said. This provides a rare glimpse into the universe’s earliest chapter. The findings, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, build…

Computer simulations reveal how water separates into high-density and low-density liquids Water is unique. It is one of the only substances that can exist in nature as a solid, liquid and gas at the same time under ambient conditions (think of solid ice over a pond, which is liquid underneath while storm clouds float overhead). It is also one of the only substances whose solid form is less dense than its liquid — this is why ice floats. Now scientists…

By Leah Shaffer Much of cell behavior is governed by the actions of biomolecular condensates: building block molecules that glom together and scatter apart as needed. Biomolecular condensates constantly shift their phase, sometimes becoming solid, sometimes like little droplets of oil in vinegar, and other phases in between. Understanding the electrochemical properties of such slippery molecules has been a recent focus for researchers at Washington University in St. Louis. In research published in Nature Chemistry, Yifan Dai, assistant professor of…

Butterflies are disappearing in the United States. All kinds of them. With a speed scientists call alarming, and they are sounding an alarm. A sweeping new study published in Science for the first time tallies butterfly data from more than 76,000 surveys across the continental United States. The results: between 2000 and 2020, total butterfly abundance fell by 22% across the 554 species counted. That means that for every five individual butterflies within the contiguous U.S. in the year 2000,…

Recently, a collaborative research team led by Professor WANG Hui and Professor ZHANG Xin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully developed a novel carbon-coated nickel ferrite (NFN@C) nanocatalyst with significant potential in cancer therapy. The results have been published in Advanced Functional Materials. Cancer therapy has always struggled with targeting tumor cells effectively while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. Traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation often have limited precision and serious side effects….

New study finds minerals drive phosphorus release at enzyme-like rates Northwestern University researchers are actively overturning the conventional view of iron oxides as mere phosphorus “sinks.” A critical nutrient for life, most phosphorus in the soil is organic — from remains of plants, microbes or animals. But plants need inorganic phosphorus — the type found in fertilizers — for food. While researchers traditionally thought only enzymes from microbes and plants could convert organic phosphorus into the inorganic form, Northwestern scientists previously…

UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering research created inorganic and polymer battery electrolytes simultaneously, with potential applications across chemistry Creating battery electrolytes – the component that carries the charged particles back and forth between a battery’s two terminals – has always been a tradeoff. Solid-state inorganic electrolytes move the particles extremely efficiently, but being solid and inorganic means they’re also brittle, hard to work with and difficult to connect seamlessly with the terminals. Polymer electrolytes are a dream to work…

Using first-principles calculations, a research group led by Prof. WANG Xianlong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, found that phosphorus doping is an effective way to achieve high-energy polymeric nitrogen with black-phosphorus structure (BP-N) stable at ambient pressure. The research results were published in Matter and Radiation at Extremes. Cubic gauche nitrogen with diamond-like structure and BP-N with black phosphorus structure, represented by polymeric all-nitrogen materials, are a class of high-energy density materials composed…

Quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) have made rapid progress in luminescence, efficiency, and stability, making them promising candidates for displays and solid-state lighting applications. However, achieving high-performance QLEDs with high color purity remains a persistent challenge, particularly red QLEDs, thus limiting the popularity of ultra-high definition devices. Recently, Soochow University, in collaboration with Macau University of Science and Technology and other research institutes, reported a facile high-temperature successive ion layer adsorption and reaction (HT-SILAR) strategy for the growth of high-quality,…

Scientists at Penn State have harnessed a unique property called incipient ferroelectricity to create a new type of computer memory that could revolutionize how electronic devices work, such as using much less energy and operating in extreme environments like outer space. They published their work, which focuses on multifunctional two-dimensional field-effect transistors (FETs), in Nature Communications. FETs are advanced electronic devices that use ultra-thin layers of materials to control electrical signals, offering multiple functions like switching, sensing or memory in a…

Faster identification of fish sounds from acoustic recordings can improve research, conservation efforts Coral reefs are some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems. Despite making up less than 1% of the world’s oceans, one quarter of all marine species spend some portion of their life on a reef. With so much life in one spot, researchers can struggle to gain a clear understanding of which species are present and in what numbers. In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical…

Some parts of Hawai‘i are sinking faster than others. That discovery, published recently in a study by researchers at the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa, also highlights that as sea level rises, the infrastructure, businesses, and communities in these low-lying areas are at risk of flooding sooner than scientists anticipated, particularly in certain urban areas of O‘ahu. “Our findings highlight that subsidence is a major, yet often overlooked, factor in assessments of future flood exposure,” said Kyle Murray, lead…

A new study led by researchers at Cardiff University, the University of Oxford, the University of Bristol, and the University of Michigan has revealed that two continent-size regions in Earth’s deep mantle have distinctive histories and resulting chemical composition, in contrast to the common assumption they are the same. The findings are available to read in the journal Scientific Reports. Seismologists have long known that seismic waves – generated by earthquakes – do not travel through all parts of Earth’s…

The discovery that inert helium can bond with iron could rewrite Earth’s history Researchers from Japan and Taiwan reveal for the first time that helium, usually considered chemically inert, can bond with iron under high pressures. They used a laser-heated diamond anvil cell to find this, and the discovery suggests there could be huge amounts of helium in the Earth’s core. This could challenge long-standing ideas about the planet’s internal structure and history, and may even reveal details of the…