Better microring sensors for optical applications
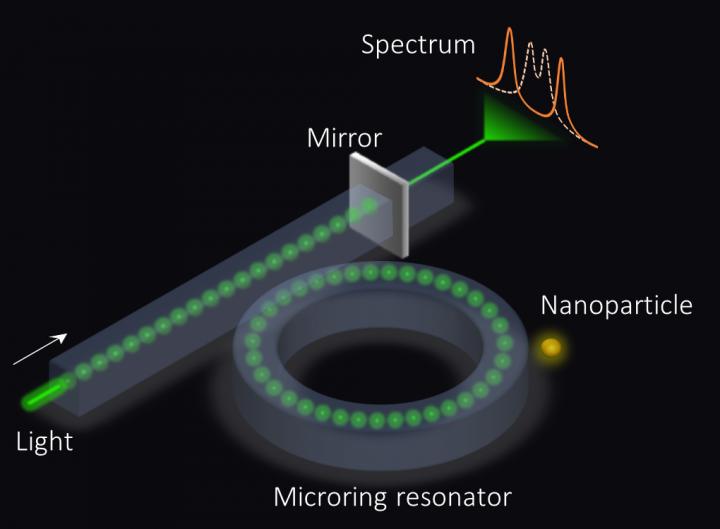
An exceptional surface-based sensor. The microring resonator is coupled to a waveguide with an end mirror that partially reflects light, which in turn enhances the sensitivity. Credit: Ramy El-Ganainy and Qi Zhong
Despite the variety of schemes used for optical sensing, they all share the same principle: The quantity to be measured must leave a “fingerprint” on the optical response of the system. The fingerprint can be its transmission, reflection or absorption. The stronger these effects are, the stronger the response of the system.
While this works well at the macroscopic level, measuring tiny, microscopic quantities that induce weak response is a challenging task. Researchers have developed techniques to overcome this difficulty and improve the sensitivity of their devices. Some of these techniques, which rely on complex quantum optics concepts and implementations, have indeed proved useful, such as in sensing gravitational waves in the LIGO project. Others, which are based on trapping light in tiny boxes called optical resonators, have succeeded in detecting micro-particles and relatively large biological components.
Nonetheless, the ability to detect small nano-particles and eventually single molecules remains a challenge. Current attempts focus on a special type of light trapping devices called microring or microtoroid resonators — these enhance the interaction between light and the molecule to be detected. The sensitivity of these devices, however, is limited by their fundamental physics.
In their article “Sensing with Exceptional Surfaces in Order to Combine Sensitivity with Robustness” published in Physical Review Letters (DOI: https:/
Exceptional Points for Exceptionally Sensitive Detection
In order to understand the meaning of exceptional points, consider an imaginary violin with only two strings. In general, such a violin can produce just two different tones — a situation that corresponds to a conventional optical resonator. If the vibration of one string can alter the vibration of the other string in a way that the sound and the elastic oscillations create only one tone and one collective string motion, the system has an exceptional point.
A physical system that exhibits an exceptional point is very fragile. In other words, any small perturbation will dramatically alter its behavior. The feature makes the system highly sensitive to tiny signals.
“Despite this promise, the same enhanced sensitivity of exceptional point-based sensors is also their Achilles heel: These devices are very sensitive to unavoidable fabrication errors and undesired environmental variations,” said Ramy El-Ganainy, associate professor of physics, adding that the sensitivity necessitated clever tuning tricks in previous experimental demonstrations.
“Our current proposal alleviates most of these problems by introducing a new system that has the same enhanced sensitivity reported in previous work, while at the same time robust against the majority of the uncontrivable experimental uncertainty,” said Qi Zhong, lead author on the paper and a graduate student who is currently working towards his doctorate degree at Michigan Tech.
Though the design of microring sensors continues to be refined, researchers are hopeful that by improving the devices, seemingly tiny optical observations will have large effects.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.153902All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A new class of cosmic X-ray sources discovered
An international team of astronomers, led by researchers from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have identified a new class of cosmic X-ray sources. The findings have been…

An open solution to improving research reproducibility
Academic and industry scientists collaborate on a new method to characterize research antibodies. Structural Genomics Consortium researchers at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University, in collaboration with scientists…

Living in the deep, dark, slow lane
Insights from the first global appraisal of microbiomes in earth’s subsurface environments. Which microbes thrive below us in darkness – in gold mines, in aquifers, in deep boreholes in the…



